What is a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) in MES?
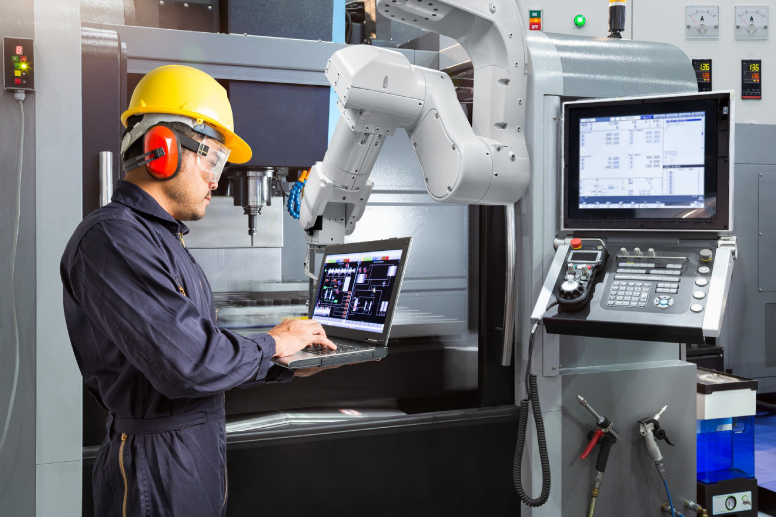

What is a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) in MES?
Equipment reliability is one of the most important factors in maintaining an efficient manufacturing operation.
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) ensures that maintenance activities are planned, tracked, and executed in a way that minimizes disruptions and maximizes uptime. Manufacturing facilities depend on these systems to automate work orders, manage asset lifecycles, and integrate maintenance workflows with production schedules.
The ability to monitor equipment health in real time and schedule proactive maintenance helps manufacturers prevent costly breakdowns and extend machine lifespan. A CMMS in manufacturing reduces maintenance costs, improves compliance, and enhances workforce efficiency. When integrated with a manufacturing execution system (MES), it creates a seamless connection between production and maintenance teams, ensuring that equipment remains operational without impacting output.
Key Features of CMMS Software in MES
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) plays a vital role in manufacturing execution systems (MES) by ensuring seamless maintenance operations, reducing equipment failures, and supporting continuous production. The right CMMS software provides essential tools to automate maintenance workflows, track asset performance, and optimize resource management. These features improve plant efficiency, extend machine lifespan, and help manufacturers meet compliance requirements.
- Automated Work Order Management: Generates, assigns, and tracks maintenance tasks, ensuring technicians receive real-time alerts for inspections and repairs. Automated workflows reduce manual scheduling errors, improve technician efficiency, and promptly address high-priority repairs.
- Preventive and Predictive Maintenance: Uses historical performance data, sensor readings, and condition-based monitoring to schedule maintenance activities before failures occur. This proactive approach minimizes costly unplanned downtime and prevents extensive damage to equipment.
- Asset Tracking and Equipment Management: Maintains a centralized database for machinery, tools, and infrastructure, allowing manufacturers to track usage, maintenance history, and depreciation. Keeping accurate records improves asset utilization and helps maintenance teams make informed repair or replacement decisions.
- Spare Parts and Inventory Control: Monitors stock levels, tracks usage patterns, and automates reordering processes to prevent supply shortages. Having the right spare parts available reduces repair wait times, ensuring minimal disruption to production.
- Failure Analysis and Root Cause Reporting: Identifies recurring issues by analyzing failure patterns and maintenance records. Data-driven insights help maintenance teams implement long-term solutions that reduce repeated breakdowns and lower repair costs.
- Compliance and Audit Support: Tracks maintenance records, inspection reports, and calibration logs to meet industry-specific regulatory requirements. Built-in compliance tools streamline audit preparation, ensuring manufacturers have accurate documentation readily available.
- Mobile Access for Maintenance Teams: Provides technicians with mobile-friendly platforms to receive work orders, log maintenance activities, and update asset information in real-time. Mobile CMMS solutions improve response times and reduce communication delays.
- IoT and Sensor-Based Monitoring: Integrates with connected devices and industrial sensors to monitor equipment performance in real-time. Automated alerts notify maintenance teams of irregularities, predictive maintenance that prevents equipment failures.
- Customizable Dashboards and Reporting: Offers data visualization tools that help plant managers analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), track maintenance efficiency, and improve resource allocation. Custom reports provide insights into work order completion rates, asset reliability, and maintenance costs.
- Integration with MES and ERP Systems: Ensures seamless data exchange between maintenance, production, and business operations. Connecting CMMS software with MES and ERP platforms allows manufacturers to synchronize maintenance activities with production schedules, improving overall workflow efficiency.
A CMMS in manufacturing provides essential tools to streamline maintenance operations, prevent equipment failures, and improve cost control. These features help manufacturers optimize asset performance, minimize production disruptions, and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
The Role of CMMS in Manufacturing
A CMMS in manufacturing serves as the foundation for effective equipment maintenance, helping facilities minimize disruptions and optimize productivity. Production lines rely on machinery operating at peak efficiency, and any unexpected breakdown can result in costly delays. A computerized maintenance management system ensures that all maintenance activities are scheduled, tracked, and executed in a way that maximizes uptime while keeping repair costs under control.
Manufacturers use a CMMS to implement proactive maintenance strategies that reduce the likelihood of unplanned downtime. Equipment sensors and historical performance data allow teams to anticipate failures and take corrective action before they impact production. Maintenance workflows are automated to assign tasks based on priority, resource availability, and machine usage patterns. This level of coordination helps manufacturing plants operate with fewer disruptions and lower operational risks.
Compliance with industry regulations is another critical function of a CMMS in MES. Manufacturing industries such as medical devices, automotive, and aerospace require meticulous tracking of maintenance records, calibration schedules, and component replacements. A CMMS software simplifies compliance efforts by documenting all maintenance activities and ensuring audit trails remain accurate and current.
Benefits of Manufacturing CMMS
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) improves manufacturing efficiency by automating maintenance workflows, tracking asset performance, and reducing equipment downtime. In an industry where operational delays lead to significant costs, a well-implemented CMMS in manufacturing ensures that maintenance teams work proactively rather than reacting to unexpected failures. The following benefits help manufacturers reduce expenses, optimize resource allocation, and improve production efficiency.
- Reduced Equipment Downtime: Scheduled maintenance tasks and predictive analytics allow maintenance teams to detect potential failures before they impact production. This proactive approach ensures equipment remains operational, minimizing disruptions to manufacturing schedules and preventing revenue loss.
- Lower Maintenance and Repair Costs: Optimized maintenance schedules prevent excessive wear and tear, reducing the need for costly emergency repairs. A CMMS in MES also helps allocate maintenance resources efficiently, preventing unnecessary labor and equipment expenditures.
- Extended Asset Lifespan: Routine inspections, timely repairs, and condition-based maintenance strategies help extend the life of machinery and production equipment. A maintenance approach reduces premature replacements, protecting capital investments.
- Improved Regulatory Compliance: Manufacturing industries, including medical devices and aerospace, require strict adherence to regulatory maintenance and safety standards. CMMS software automates documentation, ensuring that maintenance records, calibration logs, and audit trails remain accurate and readily accessible.
- Increased Workforce Efficiency: Automated work orders eliminate manual scheduling errors, ensuring technicians receive precise instructions based on equipment priorities. Mobile access to maintenance records allows teams to complete tasks more efficiently and respond to urgent repairs without delays.
- Optimized Spare Parts and Inventory Management: Automated stock level tracking ensures critical spare parts remain available. A manufacturing CMMS prevents overstocking while reducing risks associated with parts shortages, ensuring that repairs are completed on time.
- Better Equipment Performance Monitoring: IoT sensors and MES data provide real-time insights into machine conditions. Maintenance teams can rely on data-driven triggers for servicing, reducing reliance on static maintenance schedules that may not align with equipment needs.
- Enhanced Data Analytics and Reporting: Custom reports and dashboards help manufacturers track maintenance costs, technician productivity, and asset reliability. Data-driven insights support better long-term maintenance planning and strategic rationale.
- More substantial Safety and Risk Management: Regular maintenance inspections reduce the likelihood of equipment malfunctions that could pose safety hazards to employees. A CMMS software ensures that machinery remains in optimal working condition, lowering the risk of workplace incidents.
- Seamless Integration with Production Workflows: A CMMS in MES connects maintenance activities with production schedules, ensuring that planned maintenance does not interfere with critical manufacturing processes. Coordinated workflows improve efficiency without sacrificing output.
A CMMS in manufacturing ensures that production facilities remain efficient, safe, and cost-effective. Manufacturers improve asset reliability by centralizing maintenance operations and automating workflows, reducing unexpected expenses and compliance risks.
Integrating CMMS with MES
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) becomes more effective when integrated with a manufacturing execution system (MES). This connection allows manufacturers to align maintenance activities with production schedules, reducing unplanned downtime and improving overall operational efficiency. An integrated system ensures real-time asset performance monitoring, providing maintenance teams with data-driven insights to schedule preventive maintenance without disrupting manufacturing processes.
Seamless integration between CMMS software and an MES improves communication between maintenance and production teams. Equipment health data flows directly into the CMMS, allowing maintenance teams to prioritize repairs based on asset conditions rather than relying solely on time-based schedules. This coordination reduces production stoppages and prevents unnecessary maintenance activities, optimizing machine uptime and resource allocation.
Real-Time Equipment Monitoring
Machine performance data captured by IoT sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and MES platforms feed directly into the CMMS, allowing maintenance teams to assess asset health in real-time. If a piece of equipment starts showing irregular patterns, automated alerts trigger maintenance requests before failures occur. This prevents unexpected breakdowns while reducing unnecessary preventive maintenance, ensuring resources are used efficiently.
Automated Work Order Scheduling
An integrated system generates work orders based on machine conditions, production requirements, and technician availability. Maintenance tasks are scheduled in coordination with manufacturing workflows, ensuring that planned servicing does not disrupt critical operations. This approach eliminates the inefficiencies of manual scheduling and ensures that equipment receives service at the optimal time.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reporting
Manual data entry often leads to inconsistencies and errors that compromise maintenance efficiency. A CMMS in MES eliminates these challenges by automatically recording maintenance logs, repair history, and asset performance data. Accurate reporting gives maintenance managers insights into failure trends, labor efficiency, and cost-saving opportunities, improving long-term maintenance planning.
Optimized Spare Parts and Inventory Control
Connecting CMMS software with an MES directly links maintenance needs and spare parts inventory. Automatic inventory tracking ensures that necessary components are available before a maintenance task begins, reducing delays caused by missing parts. This also prevents overstocking, reducing inventory holding costs while providing critical supplies are always on hand.
Better Compliance and Audit Readiness
Manufacturers in regulated industries must maintain accurate maintenance records for compliance audits. An integrated CMMS in manufacturing streamlines this process by documenting all inspections, repairs, and calibrations in a centralized system. This improves audit readiness and helps manufacturing facilities meet regulatory standards without the burden of manual documentation.
A CMMS integrated with MES provides manufacturers with a connected maintenance strategy that enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and extends asset lifespan. The ability to track machine health, automate scheduling, and optimize inventory ensures that maintenance operations align with production goals, improving overall plant performance.
Choosing the Right CMMS Software for MES
Selecting a computerized maintenance management system that integrates effectively with an MES requires careful evaluation of key factors that impact operational efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Manufacturing operations rely on a CMMS that automates maintenance workflows and aligns with existing production processes.
Compatibility with MES software is essential for seamless data exchange between maintenance and production teams. A system that integrates with IoT devices, machine sensors, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms ensures real-time equipment monitoring and accurate maintenance tracking. Cloud-based deployment options offer flexibility by reducing on-site infrastructure costs while providing secure remote access to maintenance records.
User-friendly interfaces and mobile accessibility improve adoption rates among maintenance teams. A well-designed CMMS allows technicians to access work orders, submit reports, and update asset records from any location. Customization options further enhance usability, allowing manufacturers to tailor features such as automated scheduling, compliance tracking, and spare parts management to fit their specific needs.
Scalability is another important factor when selecting a CMMS in manufacturing. A system that supports multiple facilities, production lines, and asset categories ensures long-term usability as business operations expand. Generating detailed reports and analytics also enhances maintenance planning, helping manufacturers optimize performance and reduce operational risks.
EAM vs CMMS: Key Differences
The main difference between an enterprise asset management (EAM) system and a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) lies in their scope and functionality. A CMMS focuses on maintenance-related tasks, while an EAM provides a broader approach to asset management, covering the entire lifecycle of equipment from procurement to disposal.
| Feature | CMMS | EAM |
| Primary Focus | Maintenance scheduling and tracking | Full asset lifecycle management |
| Scope | Equipment maintenance and repairs | Procurement, maintenance, and asset utilization |
| Integration | Works with MES and maintenance teams | Connects with ERP, MES, and financial systems |
| Asset Lifecycle | Limited to the operational phase | Covers acquisition, operation, and decommissioning |
| Inventory Management | Tracks spare parts for maintenance | Manages asset-related inventory and procurement |
| Compliance Support | Ensures regulatory maintenance tracking | Covers audits, compliance reporting, and documentation |
A CMMS in manufacturing is primarily designed to manage maintenance operations, focusing on scheduling, work orders, and spare parts tracking. It helps manufacturers prevent downtime and maintain regulatory compliance through detailed maintenance logs and automated workflows.
An EAM system takes a more comprehensive approach, tracking assets throughout their lifecycle, from initial acquisition to retirement. This system integrates with financial and procurement modules, making it a better choice for manufacturers that require enterprise-wide asset management.
Future Trends in CMMS for Manufacturing
Advancements in computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) software continue to improve manufacturers' management of maintenance operations, reduce downtime, and optimize asset performance. As manufacturing facilities adopt more innovative technologies, CMMS in MES solutions incorporate automation, real-time analytics, and predictive capabilities to improve efficiency. The following trends are shaping the future of CMMS software in manufacturing.
- AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance: Artificial intelligence (AI) analyzes machine performance data to identify patterns that indicate potential failures. Instead of relying on fixed maintenance schedules, AI-driven insights help maintenance teams anticipate issues before they lead to breakdowns, improving equipment reliability and reducing repair costs.
- IoT-Connected Maintenance Systems: Industrial IoT (IIoT) devices collect real-time sensor data from machines, continuously monitoring temperature, vibration, and energy consumption. A CMMS in manufacturing processes this data and generates automated alerts when equipment conditions deviate from normal operating ranges, allowing maintenance teams to act before failures occur.
- Cloud-Based CMMS Deployment: Cloud-based CMMS software allows manufacturers to manage maintenance operations without requiring extensive on-site infrastructure. Cloud solutions offer better accessibility for maintenance teams, secure data storage, automatic updates, and the ability to scale across multiple facilities without expensive hardware investments.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for Maintenance Support: AR technology assists technicians by overlaying real-time visual instructions onto equipment during inspections and repairs. This helps reduce downtime, minimize human errors, and improve training for new maintenance personnel, ensuring tasks are performed correctly without delays.
- Mobile CMMS Applications for On-the-Go Maintenance: Maintenance teams benefit from mobile-friendly CMMS software that provides instant access to work orders, asset records, and real-time machine data. Mobile solutions improve response times by allowing technicians to diagnose and resolve issues without being tied to a desktop interface.
- Automated Workflows and AI Chatbots: AI-powered virtual assistants help maintenance teams schedule and manage tasks by automating routine processes such as work order creation and equipment status updates. These tools reduce administrative burdens, allowing technicians to focus on critical maintenance tasks instead of manual data entry.
- Integration with ERP, MES, and Supply Chain Systems: Future CMMS solutions are improving integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and supply chain platforms. This parallel approach ensures maintenance planning aligns with production goals, inventory management, and procurement schedules, reducing downtime caused by equipment failures or spare part shortages.
- Sustainability-Focused Maintenance Strategies: Manufacturers prioritize energy-efficient and sustainable maintenance practices to reduce waste and lower operational costs. A CMMS and a capable MES can support these initiatives by tracking energy usage, optimizing maintenance schedules, and ensuring compliance with fit regulations.
- Automated Compliance and Safety Audits: Compliance tracking tools within CMMS software simplify audits by maintaining digital records of inspections, certifications, and regulatory maintenance requirements. Automation reduces non-compliance risk while ensuring that all equipment remains appropriately working.
Advancements in CMMS technology are reshaping maintenance strategies by improving efficiency, increasing automation, and reducing costs. Combining AI, IoT, and real-time data analytics ensures manufacturers can optimize maintenance operations while keeping production lines running smoothly.
Manufacturers worldwide are adopting digital solutions to improve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver smart connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) automates maintenance tracking, work order scheduling, and asset management, reducing downtime in manufacturing.
- Integrating CMMS software with an MES ensures seamless coordination between maintenance and production, improving efficiency and reducing operational risks.
- Predictive maintenance powered by IoT and AI helps manufacturers schedule repairs based on real-time equipment data, preventing costly failures.
- Compliance tracking within a CMMS in manufacturing simplifies audits by maintaining digital records of maintenance activities, inspections, and regulatory requirements.
- Cloud-based CMMS solutions provide manufacturers with remote access, automated updates, and scalable deployment, making maintenance operations more efficient and cost-effective.
FAQs
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) is a software tool that automates maintenance tracking, schedules repairs, and manages asset lifecycles. It helps manufacturers reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and optimize maintenance resources.
A CMMS in MES connects maintenance activities with production schedules, ensuring real-time equipment monitoring and automated work order management. This integration helps maintenance teams prevent disruptions while optimizing machine uptime.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics rely on CMMS software to maintain regulatory compliance, improve asset reliability, and reduce maintenance costs. Any industry that depends on continuous production benefits from a CMMS.
Predictive maintenance in a CMMS in manufacturing uses IoT sensors and historical performance data to identify early signs of wear or failure. Maintenance tasks are scheduled based on actual asset conditions, reducing unnecessary servicing and preventing unexpected breakdowns.
A manufacturing CMMS lowers maintenance costs by preventing equipment failures, reducing emergency repairs, and optimizing spare parts inventory. Automated maintenance scheduling ensures resources are used efficiently, helping manufacturers control expenses while improving productivity.
How 42Q is Shaping the Next Era of Manufacturing

Building a Smarter, Greener Future
How 42Q is Shaping the Next Era of Manufacturing
As we approach Hannover Messe, the manufacturing world is buzzing with anticipation. It’s a time to reflect on where the industry is headed and how we can tackle the challenges of tomorrow. At 42Q, we’ve spent the past year working closely with manufacturers to address two of the most pressing issues facing the industry today: sustainability and the intelligent use of technology.
This isn’t about chasing trends, it’s about solving real problems. Manufacturers are under pressure to do more with less: less waste, less downtime, and less complexity. At the same time, they need to stay competitive in a rapidly changing landscape. That’s where we come in. Over the past 12 months, we’ve made significant strides in helping manufacturers achieve operational excellence while building a foundation for a more sustainable future.
Sustainability: It’s a Goal, and a Journey that requires Focus
Let’s be honest… sustainability isn’t just a nice-to-have anymore. It’s a business driver. But for many manufacturers, the path to sustainability isn’t always clear. How do you reduce waste without sacrificing efficiency? How do you optimize resource use without overhauling your entire operation? These are the questions we’ve been working to answer.
Data as the Foundation for Sustainable Manufacturing
At 42Q, we believe that sustainability starts with visibility. You can’t improve what you can’t measure. That’s why we’ve focused on giving manufacturers the tools to see their operations clearly—from energy use to material waste to equipment performance.
Our Connected Manufacturing platform, built on AWS, pulls data from across the production floor and beyond, giving manufacturers a unified view of their operations. This isn’t just about collecting data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights. For example, by analyzing cycle times and defect rates, manufacturers can pinpoint inefficiencies and reduce waste. By monitoring energy consumption, they can identify opportunities to cut costs and lower their environmental impact.
Modular Solutions for Sustainable Growth
Another way we’re helping manufacturers build sustainability into their operations is through our composable MES architecture. Traditional manufacturing systems often come with a lot of unnecessary baggage—features you don’t need, complexity you don’t want, and costs you can’t justify. Our modular approach lets manufacturers build a system that’s tailored to their specific needs, without the bloat.
This isn’t just good for the bottom line; it’s good for the planet. By only using what you need, you reduce waste—both in terms of resources and energy. And because the system is designed to grow with you, it ensures that sustainability is built into your operations from the ground up.
AI in Manufacturing: Not Just the Hype, But Real Value
There’s a lot of talk about AI in manufacturing, and frankly, a lot of it is overhyped. But when applied thoughtfully, AI can deliver real value. Over the past year, we’ve been working to integrate AI into our platform in ways that actually make a difference for manufacturers.
Arthur: Making AI Work for You
One of our proudest accomplishments this year has been the rollout of Arthur, our AI-powered assistant. Arthur is a practical tool designed to make life easier for manufacturers. Think of it as a knowledgeable colleague who’s always there to help. Need to troubleshoot a machine? Arthur can guide you through it. Looking for real-time production data? Arthur can pull it up in seconds.
What makes Arthur truly valuable is its ability to streamline workflows and reduce downtime. By providing instant access to critical information, Arthur helps manufacturers make faster, smarter decisions. And because it’s powered by Amazon Bedrock, it’s constantly learning and improving, ensuring that it stays relevant as your needs evolve.
AI Beyond the Hype: Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
Beyond Arthur, we’re also exploring how AI can be used to tackle some of the biggest pain points in manufacturing. For example, predictive maintenance is a game changer for reducing downtime and extending the life of equipment. By analyzing data from sensors and historical performance, AI can predict when a machine is likely to fail—before it happens. This not only saves time and money but also reduces the waste associated with unexpected breakdowns.
Similarly, AI can play a key role in quality control. By analyzing production data in real time, AI can detect defects early in the process, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products make it to market. These aren’t futuristic ideas—they’re practical applications of AI that are delivering real results today.
What We’ve Achieved: A Year of Progress
Looking back over the past 12 months, we’re proud of what we’ve accomplished. Here are a few highlights:
- Connected Manufacturing: We’ve helped manufacturers gain a unified view of their operations, enabling them to make smarter, more sustainable decisions.
- Arthur: Our AI-powered assistant has become an indispensable tool for manufacturers, streamlining workflows and reducing downtime.
- Composable MES: Our modular approach has given manufacturers the flexibility they need to build systems that grow with them, without unnecessary waste or complexity.
- Strategic Partnerships: We’ve strengthened our collaborations with industry leaders, ensuring that our customers have access to the best tools and expertise available.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next for 42Q?
As we head into Hannover Messe, we’re more committed than ever to helping manufacturers navigate the challenges of tomorrow. Sustainability and AI will continue to be key focus areas, but we’re also looking at new ways to drive efficiency, reduce complexity, and empower manufacturers to do their best work.
We’re excited to share our latest innovations at the show, and we look forward to connecting with manufacturers who are ready to take their operations to the next level. Because at the end of the day, our goal is to help manufacturers build a smarter, greener, and more efficient future.
The Future of Automotive Manufacturing and MES

The Future of Automotive Manufacturing and MES
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are forming automotive production, improving efficiency, quality, and traceability across the factory floor.
As manufacturing complexity increases, companies must manage production schedules, reduce waste, and meet regulatory requirements while maintaining cost control. MES bridges the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and factory operations, providing real-time data, automation, and process optimization. Automotive manufacturers adopting MES gain improved visibility, streamlined workflows, and enhanced production capabilities, ensuring they meet the growing industry with greater precision and reliability.
What is Automotive Manufacturing in MES?
Automotive manufacturing involves complex processes that form raw materials into fully functional vehicles. This industry relies on precision engineering, supply chain coordination, and quality control to ensure production efficiency and product reliability. Manufacturers seek solutions to enhance operations while reducing costs and production timelines as technology advances.
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) plays an essential role in modern automotive production by bridging the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and factory floor operations. MES provides real-time monitoring, data collection, and process automation, helping manufacturers optimize production workflows, improve traceability, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. With increasing efficiency and scalability, MES solutions are now essential for manufacturers looking to streamline operations and meet customer expectations.
Benefits of MES in Automotive Manufacturing
Automobile manufacturers must maintain high production standards while adapting to shifting market conditions. MES improves factory operations by providing digital tools that track performance, optimize workflows, and enhance overall productivity. These benefits help manufacturers lower costs, reduce errors, and maintain consistency throughout production.
- Production efficiency: MES automates data collection, reducing manual errors and ensuring accurate process tracking. This improves workflow efficiency and minimizes production downtime.
- Quality control: Real-time monitoring allows manufacturers to detect and address defects before they escalate, improving product quality and reducing waste.
- Traceability and compliance: MES provides full product traceability, recording each manufacturing process step. This helps meet regulatory requirements and improves audit readiness.
- Workforce optimization: Operators receive digital work instructions, reducing training time and enhancing worker efficiency on the factory floor.
- Supply chain visibility: MES integrates with ERP and other business systems, providing better visibility into material availability and production schedules. This improves planning and reduces delays.
- Cost reduction: Process automation and predictive maintenance reduce material waste, energy consumption, and unplanned downtime, lowering production costs.
- Scalability: MES supports multi-plant operations, allowing manufacturers to standardize processes across multiple facilities while maintaining centralized control.
Manufacturers implementing MES gain better control over production while improving agility in responding to operational challenges. These advantages make MES an essential tool for automotive companies looking to improve efficiency and maintain high-quality manufacturing standards.
Examples of MES in Automotive Manufacturing
Manufacturers rely on MES to improve efficiency, maintain product quality, and meet production goals. The system integrates with factory operations to support automation, provide real-time insights, and improve traceability. These capabilities address specific challenges in automotive manufacturing, ensuring consistent results across production lines.
1. Digital Work Instructions for Assembly Processes
Automotive production involves assembling thousands of components with precision. MES provides digital work instructions, guiding operators through each step with real-time updates. This reduces errors, minimizes rework, and ensures each vehicle meets quality standards. Operators can also receive automated alerts for process deviations, preventing defects before they affect production.
2. Production Monitoring and Performance Analytics
Factory performance depends on accurate data collection and analysis. MES tracks production rates, machine uptime, and operator efficiency, providing manufacturers with real-time insights into performance metrics. These analytics help identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing process adjustments that improve production speed and output quality.
3. Traceability for Compliance and Quality Assurance
Automotive manufacturing requires complete traceability of parts and materials to meet industry regulations. MES records each step of production, capturing data on material origins, assembly processes, and quality checks. If a defect occurs, manufacturers can trace the issue back to its source and take corrective action, reducing the risk of recalls and compliance violations.
4. Automated Inventory and Supply Chain Integration
Supply chain coordination is essential to prevent material shortages and production delays. MES integrates with inventory management systems, tracking material usage in real time and automating restocking processes. This prevents overstocking or understocking issues, ensuring materials arrive at the right time to maintain production schedules.
5. Predictive Maintenance to Reduce Downtime
Equipment failures cause unplanned downtime, delaying production and increasing costs. MES uses predictive maintenance tools to monitor machine performance and detect potential failures before they happen. Automated alerts notify maintenance teams when repairs or servicing are needed, preventing breakdowns and extending equipment lifespan.
Automotive manufacturers rely on MES to enhance production processes, improve quality control, and optimize resource allocation. These applications make MES a critical tool for increasing efficiency while reducing costs and minimizing operational risks.
Challenges in Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive manufacturers face complex operational challenges that affect production efficiency, cost control, and regulatory compliance. Meeting industry requirements while maintaining high output levels requires advanced solutions to manage factory operations effectively. MES helps address these obstacles by providing visibility, automation, and process control.
- Supply chain disruptions: Material shortages, supplier delays, and logistical constraints slow production. Manufacturers must adjust schedules and inventory levels to avoid production halts.
- Quality assurance and defect management: Identifying defects early in the process reduces rework and scrap costs. Without a formed tracking system, maintaining consistent product quality becomes difficult.
- Equipment downtime and maintenance inefficiencies: Unexpected equipment failures lead to production stoppages, increasing costs and delaying deliveries. Predictive maintenance and performance monitoring help minimize unplanned downtime.
- Regulatory compliance and traceability: Automotive manufacturers must meet strict safety regulations. Tracking materials, production steps, and testing data ensure compliance while reducing the risk of recalls.
- Production scalability: Expanding production capacity requires standardizing processes across multiple facilities. Without centralized control, scaling operations lead to inconsistencies and inefficiencies.
- Workforce training and process standardization: Operator errors and inefficient workflows reduce production speed. Digital work instructions and automated process controls improve training effectiveness and operational consistency.
- Energy consumption and sustainability requirements: Reducing waste and improving energy efficiency helps manufacturers lower costs and meet goals. Process optimization and resource monitoring provide better control over energy usage.
Manufacturers that address these challenges improve production efficiency, product quality, and overall operational stability. MES provides solutions that help factories optimize resources, reduce costs, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
How to Improve Efficiency in Automotive Manufacturing with MES
Manufacturers rely on MES to improve production efficiency, reduce operational risks, and optimize factory performance. The system provides data-driven insights, automation tools, and real-time monitoring to streamline processes. These capabilities help factories maintain quality while minimizing costs and production delays.
Automating Data Collection and Process Tracking
Manual data entry slows production and increases the risk of errors. MES automates data collection, capturing real-time production metrics from machines, sensors, and operators. This ensures accurate tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle times, defect rates, and machine utilization. Automated data reporting allows manufacturers to identify inefficiencies and adjust processes to improve productivity.
Optimizing Production Scheduling and Resource Allocation
Balancing production schedules with material availability and workforce capacity prevents delays and inefficiencies. MES synchronizes scheduling with inventory and labor management systems, ensuring that materials arrive on time and operators follow optimized workflows. This reduces bottlenecks, minimizes idle time, and maximizes overall production output.
Enhancing Quality Control with Real-Time Monitoring
Defects impact production costs and customer satisfaction. MES integrates with quality control systems to monitor product specifications, detect anomalies, and flag defects as they occur. Automated alerts notify operators when deviations happen, allowing immediate corrective actions. This reduces waste, improves product consistency, and lowers rework costs.
Implementing Predictive Maintenance to Minimize Downtime
Equipment failures lead to unplanned downtime and increased repair costs. Some MES solutions offer capabilities that address equipment downtime. These systems are capable of collecting data on machine performance and, depending on their features, may be able to predict maintenance requirements using historical data and real-time sensor inputs. This allows for proactive maintenance, with alerts being sent when servicing is needed, which can reduce unexpected failures. The goal of such features is to improve equipment reliability and prolong machine lifespans, minimizing production disruptions.
Standardizing Work Instructions for Consistent Operations
Operators need clear instructions to follow best practices and maintain process consistency. MES provides digital work instructions, ensuring each step of production is performed correctly. These instructions update in real-time based on machine status, production requirements, or regulatory changes. Standardizing workflows improves worker efficiency and reduces errors across multiple shifts and facilities.
Improving Traceability for Compliance and Supply Chain Visibility
Tracking materials, parts, and production processes ensures compliance with industry regulations. MES records each manufacturing stage, linking product batches to raw material sources and assembly data. This improves supply chain visibility and allows manufacturers to trace defects to their origin, reducing liability and improving quality control.
Reducing Waste and Improving Sustainability Efforts
Material waste and energy consumption increase production costs. Some Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) can offer features that help manufacturers track things like energy use, material waste, and how efficiently materials are being used. This data can then be used to find ways to make processes better, reduce resource consumption, and be more environmentally friendly. If done well, this can help lower costs and meet environmental rules
Manufacturers using MES gain better control over production, improving efficiency while maintaining quality and compliance standards. The system provides the tools to optimize factory operations and reduce costs in an industry.
Evolution of Automotive Manufacturing and MES
Automotive manufacturing has advanced through technological innovations that improve efficiency, safety, and product quality. MES has adapted to support these advancements, providing digital tools that connect production processes and optimize factory operations. The industry's progression reflects a shift toward automation, data-driven strategy, and integrated manufacturing systems.
- Early mass production: The introduction of assembly lines standardized vehicle manufacturing, reducing production time and increasing output. Manual processes dominated, relying on human oversight and repetitive tasks.
- Introduction of automation: Robotics and computer-controlled machinery improved precision and consistency, reducing human error and increasing production speed. Automation helped streamline repetitive tasks while improving safety and efficiency.
- Integration of digital monitoring systems: Manufacturers adopted early versions of MES to track production metrics, monitor machine performance, and manage work orders digitally. These systems provided essential real-time insights but lacked full integration capabilities.
- Expansion of data-driven manufacturing: Advanced MES platforms integrated with ERP and supply chain systems allow manufacturers to analyze performance data and optimize workflows across multiple facilities. Predictive analytics and process automation further improved production efficiency.
- Adoption of smart factories: Modern MES solutions incorporate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing to connect production lines with enterprise systems. Smart factories use real-time data to improve traceability, automate and improve production control.
- Sustainability and energy-efficient manufacturing: MES often includes tools for tracking resource consumption, optimizing energy use, and reducing material waste. These capabilities help manufacturers meet standards while lowering operational costs.
Automotive manufacturing continues to grow with advancements in automation, digital connectivity, and sustainability initiatives. MES is vital in supporting these developments, ensuring manufacturers achieve higher efficiency, lower costs, and improved production outcomes.
Key Trends in Automotive Manufacturing and MES
Manufacturers continue integrating innovative technologies into production, improving efficiency and reducing costs through automation and data-driven insights. MES is essential in optimizing factory operations by incorporating artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and predictive analytics. Cloud-based MES solutions allow greater scalability and system accessibility, reducing the need for expensive on-premise infrastructure. Sustainability initiatives drive the adoption of energy-efficient manufacturing practices, with an MES capable of monitoring real-time resource consumption to minimize waste. Cybersecurity measures remain a priority as factories connect more systems and data sources, ensuring that production information remains secure. MES-ERP integration strengthens business continuity, aligning production workflows with broader enterprise objectives for better inventory control, planning, and efficiency. Automotive manufacturers rely on these advancements to improve quality, reduce downtime, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Manufacturers worldwide are adopting cloud-based solutions to improve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver innovative, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- MES improves efficiency in automotive manufacturing by automating workflows, reducing downtime, and providing real-time visibility into production processes.
- Traceability features help manufacturers maintain compliance by tracking materials, components, and assembly processes throughout the production cycle.
- Predictive maintenance reduces machine failures and unplanned downtime by monitoring equipment health and scheduling repairs before breakdowns occur.
- Cloud-based MES solutions enhance scalability and flexibility by integrating factory operations across multiple facilities and improving data accessibility.
- MES-ERP integration strengthens manufacturing operations by aligning production schedules, resource planning, and inventory control with business objectives.
FAQs
MES improves efficiency by automating data collection, optimizing production scheduling, and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance. The system provides real-time monitoring, allowing manufacturers to adjust workflows, minimize bottlenecks, and maintain consistent output. With MES, production processes become more reliable, scalable, and cost-effective.
A comprehensive MES includes production tracking, quality management, resource planning, and traceability features. These components ensure real-time visibility into factory operations, helping manufacturers maintain compliance, reduce waste, and optimize machine utilization. Integrated digital work instructions also enhance operator efficiency and process consistency.
Traceability ensures compliance with safety regulations, reduces liability, and improves quality control by tracking each step in the manufacturing process. MES provides a digital record of materials, assembly processes, and testing data, allowing manufacturers to quickly identify and correct defects. This level of oversight helps prevent costly recalls and production delays.
MES uses machine data and sensor inputs to detect potential equipment failures before they happen. Predictive maintenance strategies reduce unplanned downtime, extend machine lifespan, and lower repair costs. By analyzing performance trends, MES ensures maintenance teams receive timely alerts for servicing, improving overall equipment efficiency.
MES focuses on real-time production management, process automation, and shop-floor monitoring, while ERP handles higher-level business operations like finance, procurement, and supply chain management. MES works with ERP to provide manufacturers with complete operational visibility, ensuring factory processes align with business goals.
15 MES Applications by Industry

15 MES Applications by Industry
Manufacturers constantly seek ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain high-quality production standards.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide a critical solution by integrating real-time monitoring, automation, and data analytics into production workflows. These applications help manufacturers across various industries track production, optimize resource utilization, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. With the ability to reduce waste, improve traceability, and enhance operational control, MES applications play a key role in modernizing manufacturing and driving long-term growth.
Importance of MES in Manufacturing
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play an essential role in modern production by connecting, monitoring, and controlling complex manufacturing processes. These systems bridge the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) and production equipment, ensuring accurate data flow and operational efficiency. As industries strive for greater agility, MES applications provide real-time insights that help you minimize downtime, improve quality, and maximize production output.
Integrating MES applications supports key operational areas, including production scheduling, traceability, quality management, and resource allocation. MES applications make data-driven by providing a centralized view of manufacturing activities, reducing errors, and optimizing workflows. This level of control is significant for industries that rely on precision and compliance, such as automotive, medical devices, and aerospace.
Beyond immediate operational improvements, MES applications also contribute to long-term scalability and cost reduction. With greater visibility into production processes, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, enhance workforce productivity, and respond more effectively to fluctuations. These advantages make MES applications a critical investment for companies looking to optimize their operations and remain adaptable in data-driven manufacturing.
15 MES Applications by Industry
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide essential tools for industries that require precision, compliance, and efficiency in production. These applications help manufacturers monitor production in real-time, automate quality control, and improve operational workflows. Below are 15 MES applications categorized by industry, each addressing unique challenges while optimizing manufacturing processes.
Automotive Industry
Automotive manufacturers rely on MES applications to manage complex assembly lines, track components, and improve production efficiency. These systems help optimize workflows, minimize defects, and improve compliance with regulatory standards.
1. Real-Time Production Monitoring
Production inefficiencies result in lost time and increased operational costs. MES applications track production in real-time, collecting data from machinery and operators to identify bottlenecks, optimize throughput, and reduce delays. Manufacturers gain complete visibility into work orders, cycle times, and output, allowing quick adjustments that improve production efficiency.
Effective production monitoring also helps reduce scrap and rework. Immediate alerts notify operators of quality deviations, preventing defective parts from advancing further in the assembly process. This improves overall product consistency and reduces material waste.
2. Quality Assurance and Defect Tracking
Automotive manufacturers must maintain strict quality control throughout production. MES applications integrate with inspection systems to detect defects at early stages, preventing faulty parts from reaching final assembly. Real-time defect tracking making manufacturers to analyze failure trends, improving quality processes over time.
Detailed defect reports allow teams to implement corrective actions quickly, reducing scrap rates and minimizing the risk of expensive recalls. Capturing quality data at every step helps ensure compliance with automotive safety regulations while maintaining high production standards.
3. Traceability and Component Serialization
Manufacturers must track each component through the production cycle to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. MES applications provide full traceability by assigning serial numbers to components and recording their history, from supplier sourcing to final vehicle assembly.
Serialized traceability simplifies recall management by identifying specific batches of defective parts rather than requiring full-scale product recalls. This improves accountability while reducing liability risks for manufacturers and suppliers.
4. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management
Managing inventory efficiently prevents production delays and minimizes unnecessary costs. MES applications coordinate material deliveries with production schedules, ensuring that parts arrive when needed. This reduces excess stock, prevents shortages, and optimizes warehouse space.
Automated inventory tracking helps reduce lead times and improves supply chain reliability. Keeping inventory levels aligned with production grow minimizes waste while supporting lean manufacturing principles.
5. Workforce and Task Allocation
Optimizing labor allocation improves productivity and reduces idle time. MES applications assign tasks based on worker availability, skill levels, and production priorities, ensuring that each station operates efficiently.
Smart scheduling improves resource utilization by aligning work assignments with operational needs. Skill-based allocation reduces human errors, while digital work instructions provide operators with step-by-step guidance to improve efficiency.
Medical & Pharmaceutical Industry
Strict regulatory requirements make MES applications essential in medical and pharmaceutical manufacturing. These systems ensure compliance, track product quality, and improve documentation accuracy.
6. Electronic Batch Record (EBR) Management
Paper-based record-keeping increases the risk of human errors and non-compliance. MES applications digitize batch records, ensuring accurate and complete documentation for every production run.
Electronic batch records improve traceability and simplify audit preparation. Manufacturers can store, retrieve, and update production data in a centralized system, reducing paperwork and ensuring compliance with industry standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
7. Real-Time Process Monitoring
Precise control over production conditions ensures product safety and consistency. MES applications monitor temperature, pressure, and humidity in real-time, preventing deviations that could compromise product integrity.
Automated alerts notify operators of variations in process conditions, reducing the risk of contamination or defective batches. This level of monitoring supports Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and improves regulatory compliance.
8. Regulatory Compliance Support
Regulatory agencies require detailed production records and audit trails. MES applications automate compliance reporting, reducing the manual effort needed to prepare for audits.
Automated compliance tracking helps ensure that all manufacturing processes adhere to industry regulations. Digital logs provide transparency and prevent errors in documentation, reducing the risk of regulatory violations.
9. Equipment Calibration and Maintenance Tracking
Maintaining properly calibrated equipment is essential for consistent product quality. MES applications track calibration schedules and log maintenance activities to prevent equipment failures.
Automated maintenance reminders reduce unplanned downtime and extend asset lifespan. Preventive maintenance ensures machines operate at peak performance, supporting reliable and repeatable production processes.
10. Batch and Product Traceability
Tracking raw materials and final products improves product safety and recall management. MES applications provide complete traceability from ingredient sourcing to final packaging.
Automated traceability reduces risks associated with contamination or defects. When recalls are necessary, manufacturers can quickly identify affected batches, reducing financial losses and protecting consumer safety.
Food and Beverage Industry
Food manufacturers use MES applications to improve safety, maintain quality standards, and optimize production workflows. These systems provide real-time process monitoring and automate compliance tracking.
11. Recipe and Ingredient Management
Precision in ingredient measurements ensures product consistency. MES applications store digital recipes and track ingredient usage to prevent formulation errors.
Standardized recipe management reduces variability between batches. Automated recipe enforcement helps manufacturers maintain uniform product quality across different production facilities.
12. Food Safety and Compliance Tracking
Food manufacturers must meet strict safety regulations. MES applications monitor processing conditions, track ingredient sources, and automate compliance reporting.
Automated food safety tracking prevents contamination risks and simplifies regulatory audits. Digital logs provide proof of compliance with safety standards, reducing legal and financial risks for manufacturers.
13. Production Scheduling and Workflow Optimization
Optimizing production workflows improves efficiency and reduces operational costs. MES applications balance workloads, align production with market, and prevent bottlenecks.
Real-time scheduling adjustments help manufacturers meet order deadlines without unnecessary delays. Better workflow management improves labor efficiency and reduces raw material waste.
14. Waste Reduction and Yield Optimization
Minimizing waste lowers costs and improves profitability. MES applications analyze production data to identify inefficiencies, allowing manufacturers to optimize ingredient usage and reduce overproduction.
Data-driven insights help manufacturers refine processes to maximize yields. Reduced food waste improves sustainability efforts while increasing operational efficiency.
15. Packaging and Labeling Verification
Accurate labeling is essential for regulatory compliance and consumer safety. MES applications automate packaging processes, verifying ingredient lists, expiration dates, and nutritional information.
Automated label verification prevents mislabeling errors, reducing product recalls. Consistent labeling ensures that consumers receive accurate information while meeting compliance requirements.
Benefits of Implementing MES Applications
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) improve production efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance product quality by providing real-time visibility and process automation. These applications support manufacturers in industries where precision, compliance, and scalability are critical. Implementing MES applications leads to measurable improvements across production lines, supply chain operations, and workforce management.
- Improved Production Efficiency: Automating workflows reduces manual data entry, minimizes human errors, and accelerates production cycles. MES applications provide real-time monitoring of manufacturing activities, allowing manufacturers to identify bottlenecks and optimize machine utilization. A data-driven approach to production management helps reduce downtime, improve throughput, and streamline daily operations.
- Enhanced Product Quality and Traceability: Tracking materials, monitoring process parameters, and logging quality inspections at every production stage ensures consistent product quality. MES applications detect deviations in real-time, allowing operators to make immediate corrections. Full traceability simplifies compliance with industry regulations and improves response times for recalls or quality-related investigations.
- Cost Reduction Through Waste Minimization: Manufacturing waste leads to unnecessary costs and inefficiencies. MES applications analyze production data to identify where waste occurs, helping manufacturers adjust processes to improve material usage. Automating defect detection and optimizing workflows reduces scrap rates while ensuring that raw materials are used efficiently.
- Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness: Industries with strict compliance requirements benefit from automated documentation and compliance tracking. MES applications generate and store digital production records, ensuring that all manufacturing data is readily available for audits. Standardized reporting reduces the risk of regulatory violations and simplifies certification processes.
- Better Workforce Utilization: Assigning tasks based on skill levels, availability, and production priorities optimizes labor resources. MES applications automate workforce scheduling, reducing idle time and improving overall productivity. Digital work instructions help operators complete tasks more efficiently, reducing training time and minimizing errors.
- Seamless Integration With Supply Chain Operations: Synchronizing production schedules with material deliveries prevents disruptions caused by shortages or excess inventory. MES applications provide real-time updates on stock levels, helping manufacturers manage materials efficiently. Improved coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors ensures that production stays aligned with orders.
- Predictive Maintenance for Equipment Reliability: Equipment downtime disrupts production and increases costs. MES applications track machine performance data, detecting signs of wear or potential failures before breakdowns occur. Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime, extends asset lifespan, and helps manufacturers maintain consistent production output.
- Scalability for Expanding Operations: Standardized processes and centralized data management allow manufacturers to scale operations without unnecessary complexity. Cloud-based MES applications provide multi-site visibility, allowing manufacturers to monitor and manage production across multiple facilities. Consistent workflows improve efficiency while supporting long-term growth.
Implementing MES applications allows manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce operational risks, and maintain high-quality production standards. These systems provide a foundation for data-driven helping companies optimize resources while meeting industry compliance requirements. MES adoption supports manufacturers in achieving greater operational control, cost savings, and long-term scalability.
Future Trends in MES Applications
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) continue to move with advancements in automation, data analytics, and cloud computing. As manufacturers seek greater efficiency, flexibility, and visibility across operations, MES applications are integrating new technologies to meet industry grows.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning improve predictive analytics in MES applications, allowing manufacturers to optimize production scheduling, identify potential failures before they occur, and enhance quality control through automated defect detection. AI-driven insights help manufacturers make data-backed decisions that improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Cloud-based MES solutions provide multi-plant connectivity, allowing manufacturers to manage global operations through a centralized platform. Cloud deployment reduces infrastructure costs while ensuring real-time access to production data from any location. This shift supports manufacturers looking for scalable, remote-accessible solutions that improve collaboration between production sites.
Integration with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is improving data collection and equipment monitoring. Smart sensors connected to MES applications provide real-time machine performance data, helping manufacturers track overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), automate maintenance scheduling, and reduce unplanned downtime.
Augmented reality (AR) and digital twin technology enhance training and troubleshooting capabilities. AR-enabled MES applications allow technicians to visualize production processes, receive step-by-step guidance, and interact with digital representations of equipment for more efficient maintenance and problem-solving.
Cybersecurity is becoming a priority as MES applications handle increasing production data. Enhanced security features, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and secure cloud storage, ensure manufacturers protect sensitive information while complying with industry regulations.
MES applications will continue integrating with emerging technologies to improve manufacturing efficiency, quality control, and supply chain coordination. As automation and data-driven processes advance, manufacturers will rely on MES solutions to maintain operational agility and optimize production.
Manufacturers worldwide embrace cloud-based solutions to achieve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver smart, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- MES applications improve production efficiency by automating workflows, reducing errors, and optimizing machine utilization to minimize downtime and maximize output.
- Real-time monitoring and quality tracking enhance product consistency by detecting defects early and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Automated inventory and supply chain management prevent material shortages and overstocking, improving operational agility and cost efficiency.
- Regulatory compliance and audit readiness are simplified through digital records, automated reporting, and process standardization.
- Predictive maintenance features reduce equipment downtime by monitoring performance data and scheduling proactive maintenance before failures occur.
FAQs
An MES application is a software solution that monitors, tracks, and controls production processes in real time. It provides manufacturers with visibility into operations, automates data collection, and optimizes production workflows to improve efficiency and quality.
MES applications reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and streamline workflows by automating production monitoring and scheduling. Real-time insights help manufacturers identify bottlenecks, allocate resources effectively, and minimize downtime to improve overall efficiency.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, food and beverage, and electronics manufacturing benefit significantly from MES applications. These sectors require precision, regulatory compliance, and real-time traceability, all of which MES applications provide.
MES applications automate documentation, track production data, and generate audit-ready reports. By maintaining digital records and enforcing process controls, MES solutions help manufacturers meet regulatory requirements in industries with strict compliance standards.
MES focuses on shop floor execution, providing real-time visibility into production processes, equipment performance, and quality control. ERP systems manage broader business functions such as finance, procurement, and supply chain management. Integrating MES with ERP ensures seamless coordination between production and enterprise operations.
What Are OEE Systems in Manufacturing?
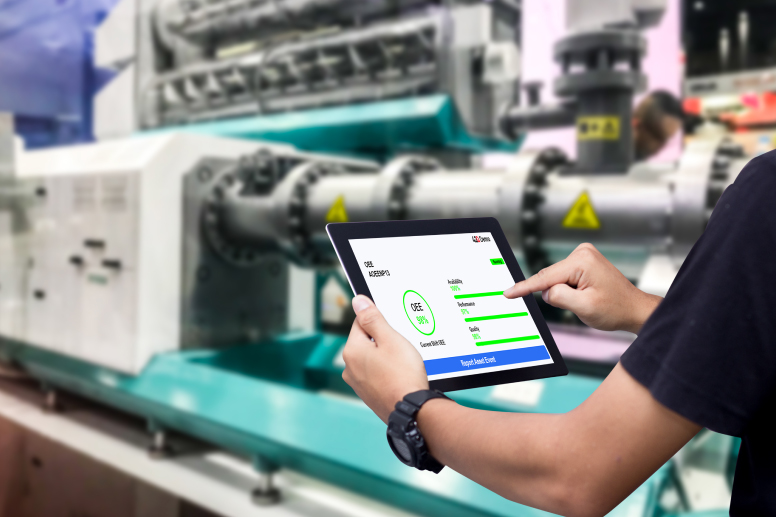

What Are OEE Systems in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers rely on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) to assess and improve production efficiency.
Measuring availability, performance, and quality helps identify bottlenecks, reduce unplanned downtime, and enhance productivity. Manufacturers struggle to maintain consistent output and operational reliability without accurate OEE tracking.
OEE systems in manufacturing provide actionable insights that allow businesses to improve machine utilization, streamline workflows, and optimize resource allocation. Understanding how to measure and apply OEE metrics reduces waste, improves product quality, and ensures production runs efficiently.
What Does OEE Stand For in Manufacturing?
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a standardized metric that quantifies manufacturing productivity by measuring how efficiently equipment operates. It evaluates three critical factors—availability, performance, and quality—to determine the percentage of planned production time that is genuinely productive. A perfect OEE score of 100% indicates flawless manufacturing: no unplanned downtime, no slow cycles, and zero defects.
Manufacturers rely on OEE to pinpoint inefficiencies, track continuous improvement initiatives, and optimize production output. By providing real-time visibility into equipment effectiveness, OEE systems in manufacturing help identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, and increase throughput. Understanding this metric is essential for improving operational efficiency and maintaining a driving edge in modern production situations.
Importance of OEE Systems in Manufacturing
OEE systems in manufacturing provide a structured approach to identifying and eliminating inefficiencies in production. Every unplanned stoppage, slow cycle, or defective product directly affects output and profitability. Without accurate data on these losses, manufacturers struggle to implement meaningful improvements. OEE systems quantify equipment effectiveness, offering clear insights into performance trends and production constraints.
Operational visibility is essential for improving production efficiency and reducing waste. OEE data helps manufacturers identify recurring downtime causes, assess equipment performance, and implement targeted maintenance strategies. Instead of reacting to breakdowns, businesses can shift to proactive measures that extend machine lifespan, optimize workforce utilization, and maximize throughput.
Key Components of OEE in Manufacturing
OEE systems in manufacturing evaluate equipment efficiency using three fundamental metrics: availability, performance, and quality. Each component identifies specific production losses and provides insight into areas requiring improvement. Understanding these factors helps manufacturers reduce downtime, optimize production speed, and improve product quality.
Availability: Minimizing Downtime and Maximizing Production Time
Availability measures the percentage of planned production time that equipment remains operational. Downtime caused by unplanned maintenance, changeovers, or raw material shortages reduces production efficiency. OEE systems track planned and unplanned stoppages, providing data that helps manufacturers address recurring issues.
Several factors contribute to availability losses, including unexpected equipment failures, lengthy setup times, and delayed material deliveries. Preventive maintenance programs, standardized changeover procedures, and better inventory management reduce disruptions. Increasing machine uptime ensures that production schedules remain consistent, improving manufacturing efficiency.
Performance: Ensuring Optimal Production Speeds
Performance evaluates how efficiently equipment operates compared to its designed capacity. Machines running at slower-than-expected speeds or experiencing frequent micro-stoppages contribute to performance losses. These inefficiencies reduce output without directly halting production, making them difficult to detect without real-time monitoring.
OEE tracking helps manufacturers identify process inefficiencies such as slow cycle times, suboptimal machine settings, and worn-out tooling. Addressing these issues improves production rates while maintaining consistent quality. Proper operator training, proactive machine adjustments, and automated process monitoring support higher performance levels.
Quality: Reducing Defects and Improving Product Consistency
Quality measures the percentage of manufactured products that meet specifications without requiring rework or scrap. Defective products lead to waste, increased costs, and additional labor for corrections. OEE systems track defect rates, providing insights into production inconsistencies and recurring quality issues.
Several factors, including improper machine calibration, inconsistent raw materials, and operator errors, contribute to quality losses. Real-time quality monitoring, automated defect detection, and process standardization help manufacturers maintain high product standards. Identifying and addressing the root causes of defects reduces material waste, improves customer satisfaction, and enhances overall production reliability.
How These Components Work Together
Availability, performance, and quality are connected, with losses in one area often affecting the others. A machine experiencing frequent downtime (availability loss) may also struggle to maintain optimal cycle times (performance loss). Likewise, running equipment at maximum speed without proper quality controls may lead to increased defects (quality loss).
OEE systems in manufacturing provide a structured approach to measuring and improving these key components. Tracking and analyzing OEE data helps manufacturers implement targeted improvements that enhance equipment reliability, increase throughput, and maintain high-quality production standards.
Benefits of Implementing OEE Systems in Manufacturing
OEE systems in manufacturing provide valuable insights that help manufacturers improve efficiency, reduce production losses, and maintain consistent product quality. Measuring availability, performance, and quality allows businesses to identify inefficiencies and take targeted actions that enhance productivity. Tracking OEE metrics provides a structured approach to minimizing downtime, improving machine reliability, and increasing output without requiring additional resources.
- Reduced Downtime and Unplanned Stoppages: Equipment failures and unexpected maintenance issues disrupt production schedules and reduce output. OEE tracking provides real-time data on recurring downtime causes, allowing manufacturers to implement proactive maintenance strategies. Predictive maintenance based on historical trends helps reduce breakdowns, ensuring machines operate reliably and production schedules remain uninterrupted.
- Increased Production Efficiency: Machines that operate below optimal speeds or experience frequent micro-stoppages lead to performance losses. OEE monitoring identifies slow-running equipment, enabling manufacturers to make necessary adjustments. Process optimization, better operator training, and automated tracking tools help improve production rates, ensuring machines perform at their designed capacity.
- Improved Product Quality and Defect Reduction: Defective products lead to material waste, rework, and increased operational costs. OEE systems track defect rates and identify patterns that indicate process inconsistencies or equipment malfunctions. Early detection of quality issues allows manufacturers to implement corrective actions before large-scale defects occur, maintaining high product standards while reducing scrap and rework expenses.
- Lower Operational Costs and Better Resource Utilization: Production inefficiency wastes valuable resources, from raw materials to labor hours. OEE data helps manufacturers optimize resource allocation by ensuring equipment operates efficiently, and workforce utilization remains balanced. Reducing material waste, minimizing energy consumption, and optimizing production workflows contribute to significant cost savings over time.
- Data-Driven Regulating for Continuous Improvement: Accurate and detailed production data allows manufacturers to identify trends and measure the effectiveness of process improvements. OEE reports provide insights into production bottlenecks, enabling businesses to implement data-backed changes that drive continuous operational improvements. Historical data tracking helps assess long-term trends and ensures sustained productivity gains.
- Sustainability and Waste Reduction: Manufacturing operations generate excess waste when inefficient processes or production defects occur. OEE tracking helps minimize unnecessary waste by improving equipment reliability, reducing defective output, and streamlining production workflows. Efficient manufacturing practices contribute to lower energy consumption and a reduced footprint, aligning with sustainability goals while maintaining cost-effective operations.
OEE systems in manufacturing provide structured insights that support efficiency improvements at every production stage. Tracking availability, performance, and quality metrics ensure manufacturers can pinpoint inefficiencies, reduce costs, and maintain a high standard of production output. Implementing OEE-driven improvements leads to measurable gains in productivity, operational stability, and long-term manufacturing success.
Real-World Applications of OEE in Manufacturing
OEE systems in manufacturing are widely used across industries to improve production efficiency, reduce downtime, and maintain high-quality standards. Manufacturers rely on OEE tracking to optimize processes, minimize losses, and ensure consistent output. Each industry applies OEE data to address specific challenges, from reducing machine failures in high-volume production to maintaining strict compliance in regulated sectors.
Automotive Production: Optimizing Assembly Line Efficiency
Automotive manufacturers depend on OEE tracking to maintain continuous production flow in high-speed assembly lines. Unplanned downtime in welding, stamping, and painting stations can cause costly delays and disrupt supply chain coordination. Monitoring availability helps manufacturers detect frequent stoppages, while performance tracking ensures robotic systems and conveyor lines run at optimal speeds. Quality metrics help identify production defects early, preventing faulty components from reaching final assembly. By applying OEE data, automotive manufacturers improve throughput while reducing waste and rework.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Ensuring Compliance and Quality
Medical device manufacturers operate under strict regulatory standards requiring precision, traceability, and consistency. OEE systems help track machine performance in critical operations such as injection molding, sterilization, and assembly. Availability data allows manufacturers to reduce downtime caused by maintenance or validation requirements, while performance monitoring ensures equipment operates within specified tolerances. Quality tracking helps detect defects in sensitive components, minimizing the risk of compliance issues and ensuring that all products meet the required specifications before distribution.
Semiconductor Fabrication: Enhancing Yield and Process Stability
Semiconductor manufacturing relies on OEE tracking to improve yield rates in highly complex and precise fabrication processes. Equipment availability is critical in wafer processing, where unexpected downtime leads to production losses and increased costs. Performance tracking ensures that lithography, etching, and deposition machines operate at optimal cycle times, reducing inefficiencies impacting product quality. Quality monitoring helps manufacturers detect process deviations that could lead to defective chips, allowing for real-time adjustments that protect overall yield.
Aerospace Component Manufacturing: Maintaining Production Reliability
Aerospace manufacturers use OEE systems to monitor production consistency in machining, composite fabrication, and surface finishing processes. Availability tracking helps reduce unplanned downtime in CNC machining and assembly operations, preventing disruptions in supply chain commitments. Performance monitoring ensures that materials such as aluminum and titanium are processed at the correct speeds to avoid defects of stress. Quality tracking supports precision manufacturing requirements, ensuring that critical aerospace components meet industry regulations and safety standards.
Industrial Equipment Manufacturing: Optimizing Multi-Line Production
Manufacturers producing heavy machinery, engines, and industrial components rely on OEE data to improve efficiency across multiple production lines. Availability tracking helps reduce production delays caused by long setup times and changeovers, while performance monitoring ensures machines operate at maximum capacity. Quality data allows manufacturers to detect recurring defects in castings, welded structures, and hydraulic components, leading to fewer warranty claims and improved product reliability.
OEE tracking provides manufacturers data-driven insights that improve efficiency, enhance quality, and support long-term operational stability. Industries implementing structured OEE measurement strategies gain higher production output, reduced waste, and more predictable manufacturing processes.
How to Effectively Measure OEE in Manufacturing
Measuring OEE in manufacturing requires a structured approach that captures accurate availability, performance, and quality data. A well-defined measurement system ensures manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, track production trends, and implement targeted improvements. Accurate OEE tracking provides a clear understanding of equipment effectiveness, helping businesses reduce downtime, improve production speed, and maintain product consistency.
- Define Equipment Availability: Availability measures the actual operating time of equipment compared to the planned production time. Calculating this metric requires subtracting all unplanned downtime, such as machine breakdowns, material shortages, and lengthy changeovers, from the total scheduled time. A lower-than-expected availability score signals recurring stoppages that must be addressed through preventive maintenance, better scheduling, or process adjustments.
- Monitor Performance Efficiency: Performance evaluates how well equipment operates at its designed speed. Machines that run slower than expected, experience frequent micro-stoppages or require frequent operator intervention reduce overall efficiency. Tracking cycle times helps manufacturers pinpoint performance issues caused by incorrect machine settings, worn-out tooling, or inconsistent material feed rates. Addressing these inefficiencies ensures machines produce at optimal speeds without compromising quality.
- Track First-Pass Quality Rates: Quality measures the percentage of products that meet specifications without requiring rework or scrap. To calculate this metric, manufacturers must track defect rates and analyze patterns in production errors. Common causes of quality losses include misaligned machine calibration, raw material inconsistencies, and operator errors. Identifying recurring quality issues requires manufacturers to implement corrective actions such as improved quality control procedures, automated defect detection, and stricter process standards.
- Use Automated Data Collection Systems: Manually tracking OEE metrics increases the risk of data errors and inconsistencies. Automated monitoring solutions, such as machine sensors, manufacturing execution systems (MES), and IoT tracking devices, provide real-time data on equipment performance. These systems capture production information more accurately, allowing manufacturers to respond to inefficiencies immediately rather than relying on retrospective analysis.
- Analyze OEE Trends and Historical Data: Measuring OEE once provides a snapshot of performance, but long-term tracking offers more profound insights into production patterns. Historical OEE data helps manufacturers assess the effectiveness of process improvements, compare performance across different shifts, and identify recurring inefficiencies. Regularly analyzing trends ensures that manufacturing operations continuously improve and that productivity gains are maintained over time.
- Set Benchmarks and Target Goals for Improvement: OEE measurement becomes more effective when manufacturers establish clear benchmarks based on industry standards or internal historical performance. Setting achievable OEE goals allows businesses to track progress and measure the success of process optimizations. Comparing OEE scores across different machines, production lines, or factory locations provides valuable insights into areas that require further refinement.
Implementing a structured OEE measurement process ensures manufacturers collect reliable data, identify inefficiencies, and improve production outcomes. Accurate tracking of availability, performance, and quality metrics supports continuous improvement efforts, helping manufacturers achieve higher efficiency and more consistent operational results.
Manufacturers worldwide are adopting data-driven solutions to improve efficiency, quality, and operational visibility. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver innovative, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital factory change. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- To assess manufacturing efficiency, OEE measures three key components—availability, performance, and quality.
- Reducing unplanned downtime through predictive maintenance and optimized changeovers improves equipment availability.
- Optimizing machine performance by addressing micro-stoppages and slow cycle times increases production output.
- Minimizing defects and rework ensures higher product quality while reducing material waste and operational costs.
- Implementing OEE tracking systems gives manufacturers data-driven insights to support continuous process improvements.
FAQs
OEE has been widely used in manufacturing since the 1980s when companies began adopting lean production methodologies. As digital tools and automation improved, OEE became a standard metric for evaluating production efficiency. Today, manufacturers rely on OEE tracking systems to optimize workflows and reduce operational losses.
OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness and is a key metric to assess manufacturing efficiency. It measures availability, performance, and quality to determine how effectively equipment is utilized. Tracking OEE helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and improve product output.
OEE systems track machine availability and analyze unplanned downtime causes such as equipment failures, long setup times, and material shortages. Manufacturers can reduce stoppages and maintain a stable production flow using predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. Preventing frequent breakdowns leads to increased uptime and higher productivity.
OEE is a comprehensive metric that combines three key factors—availability, performance, and quality—into a single effectiveness score. Unlike standalone metrics such as machine utilization or defect rate, OEE provides a holistic view of production efficiency. Using OEE alongside other key performance indicators (KPIs) gives manufacturers deeper insights into overall productivity.
Manufacturers can improve OEE scores by addressing availability losses, optimizing machine performance, and reducing quality defects. Strategies such as preventive maintenance, automated process monitoring, and workforce training help enhance efficiency. Using real-time OEE tracking systems allows businesses to make data-driven decisions that lead to continuous improvements.
7 Features of MES in Industrial Automation
7 Features of MES in Industrial Automation
Manufacturers require efficient, data-driven systems to maintain productivity and quality in industrial automation.
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) bridge the gap between enterprise planning and shop floor control, providing real-time tracking, workflow automation, and compliance management. These systems integrate with industrial automation to streamline production processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance product traceability.
As production increases, MES helps manufacturers improve efficiency while reducing errors and waste. These systems centralize production data, providing the visibility needed to make informed decisions. With advanced tracking, predictive maintenance, and seamless system integration, MES supports manufacturers in maintaining consistent operations while adapting to new production requirements.
Understanding MES in Industrial Automation
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are essential in industrial automation, as they connect production processes, track operations, and ensure data-driven decision-making. These systems bridge the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) and shop floor control, delivering real-time insights that enhance efficiency, quality, and compliance. As industrial automation expands, MES provides a scalable solution for improving productivity while maintaining strict operational standards.
MES solutions collect, analyze, and interpret production data to optimize manufacturing workflows. By offering real-time visibility into work-in-progress (WIP), machine performance, and quality assurance, MES empowers manufacturers to reduce downtime, improve throughput, and maintain consistency across operations. With increasing for traceability and regulatory adherence, MES also supports industries that require stringent documentation and compliance measures.
Benefits of MES in Industrial Automation
Manufacturers use MES to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain consistency in manufacturing processes. These systems connect production operations, providing real-time insights that support better resource management, quality control, and compliance tracking. MES also integrates with industrial automation technologies to streamline operations and minimize manual intervention, improving accuracy and reducing delays.
The benefits of MES extend across multiple areas, from optimizing equipment utilization to enhancing supply chain visibility. These advantages allow manufacturers to maintain high output levels while ensuring product reliability and regulatory adherence. MES capabilities support automation, data-driven improvements, and overall operational efficiency.
- Real-time production monitoring: MES provides continuous visibility into production operations, tracking work-in-progress (WIP), material consumption, and machine performance. Operators receive instant updates, allowing them to identify and address bottlenecks before they disrupt workflows. Real-time tracking reduces unplanned downtime, improves response times, and ensures that production schedules remain on track.
- Optimized resource utilization: Manufacturing operations depend on efficiently using materials, labor, and equipment. MES analyzes production data to identify inefficiencies and optimize resource allocation. Automated scheduling ensures that machinery operates at peak efficiency while reducing idle time. Workforce management tools help balance labor distribution, preventing production slowdowns caused by underutilized or overburdened teams.
- Improved product quality: MES enforces quality control processes, tracking defects and ensuring that inspections are performed at the correct intervals. Automated alerts notify operators when quality deviations occur, allowing immediate corrective action. Historical quality data provides insights into recurring issues, making refining processes and maintaining product consistency easier. Manufacturers in regulated industries benefit from traceability features that document compliance with industry standards.
- Streamlined compliance tracking: Manufacturing industries must adhere to strict regulatory requirements, requiring accurate documentation of production activities. MES automates compliance tracking by recording process data, material genealogy, and quality inspection results. These records support audit readiness and reduce the time spent on manual reporting. Manufacturers in aerospace, medical devices, and automotive sectors benefit from MES features that simplify regulatory adherence.
- Reduced production costs: MES helps manufacturers minimize waste, optimize inventory, and improve energy efficiency, leading to lower operating costs. Automated production tracking reduces material overuse and prevents unnecessary downtime. Data-driven process optimization further reduces expenses by identifying areas where production time and labor can be minimized without sacrificing output quality.
- Seamless data integration: MES connects with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, industrial IoT (IIoT) devices, and production machinery to centralize data collection and reporting. This integration provides a comprehensive view of manufacturing operations, ensuring managers can access accurate, real-time insights. Improved data flow between systems enhances production planning, inventory control, and supply chain management.
- Enhanced supply chain visibility: MES supports material tracking, supplier coordination, and inventory management, preventing disruptions caused by stock shortages or misaligned production schedules. Automated updates provide real-time inventory adjustments, reducing the risk of overproduction or excess storage costs. Improved supply chain coordination ensures manufacturers meet production targets while reducing logistical challenges.
Manufacturers rely on MES to improve production visibility, reduce inefficiencies, and maintain consistent quality. These benefits help production teams meet output targets while minimizing costs and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. As industrial automation advances, MES continues to be an essential tool for optimizing manufacturing operations.
7 Features of MES in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation relies on precise coordination between machines, data systems, and human operators. Manufacturing execution systems (MES) provide the digital infrastructure to synchronize production processes, track real-time performance, and ensure quality control at every stage. These systems offer an advanced level of visibility, helping manufacturers optimize efficiency, reduce errors, and improve resource management.
MES features support critical production functions, including real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and compliance tracking. As manufacturers implement automation technologies, these capabilities allow them to maintain high output levels without sacrificing product quality or regulatory adherence. MES features are fundamental to improving efficiency, consistency, and data-driven manufacturing decisions.
1. Real-time Data Tracking
Production efficiency depends on continuously monitoring materials, equipment, and process execution. MES collects and processes real-time data from production lines, providing instant insights into work-in-progress (WIP), inventory levels, and machine performance. This data allows manufacturers to make informed adjustments, preventing bottlenecks and reducing downtime.
Automated data collection eliminates manual tracking errors and ensures operators receive accurate production status reports. With real-time visibility, manufacturers can monitor throughput, detect potential disruptions, and identify opportunities for improvement. These insights allow production teams to fine-tune processes, optimize scheduling, and maintain consistent operational output.
Beyond performance tracking, MES also analyzes historical data, helping manufacturers identify patterns that impact productivity. Trends in cycle times, equipment utilization, and defect rates become more straightforward to interpret, and production teams to refine operations and reduce inefficiencies.
2. Enhanced Production Efficiency
Manufacturers depend on MES to streamline workflows and improve resource utilization. These systems automate production scheduling, work order management, and process enforcement to minimize delays and maintain consistency. Automated scheduling ensures that workstations receive the correct instructions at the right time, reducing human errors and improving throughput.
Resource allocation becomes more effective with MES, providing real-time insights into equipment availability, workforce productivity, and material consumption. This data-driven approach minimizes idle time and prevents supply chain inefficiencies that could disrupt production. MES also supports automated adjustments to production schedules based on popular fluctuations, ensuring manufacturers maintain optimal output levels without excessive inventory buildup.
Process standardization further improves efficiency. MES enforces predefined workflows, ensuring that operators follow the correct steps and adhere to established quality control measures. Consistency in production methods reduces defects and rework, improving overall efficiency while maintaining product reliability.
3. Quality Control and Assurance
Maintaining high product quality is a priority in industrial automation. MES integrates with quality management systems to track defect rates, enforce inspection protocols, and standardize compliance measures. Automated data collection helps detect quality deviations early, preventing defective products from progressing through production.
Automated alerts notify operators when production parameters fall outside acceptable ranges. Early detection allows manufacturers to take corrective action immediately, reducing waste and minimizing costly rework. Historical quality data also provides insights into recurring issues, helping manufacturers refine processes to prevent future defects.
Regulated industries benefit from MES-driven quality control, as these systems maintain electronic batch records, track material genealogy, and ensure that manufacturing processes align with industry standards. Traceability features allow manufacturers to provide detailed compliance reports, reducing the complexity of audits and regulatory reviews.
4. Supply Chain Management
Production stability depends on effective supplier coordination, inventory management systems, and manufacturing operations. MES strengthens supply chain efficiency by providing real-time updates on material consumption, supplier performance, and inventory levels. Automated tracking ensures manufacturers maintain optimal stock levels while avoiding shortages and overproduction.
Inventory synchronization is an essential function of MES, preventing production delays caused by missing materials. These systems automatically adjust stock levels based on usage rates, ensuring critical components are available when needed. Supplier coordination also improves, as MES provides insights into lead times, delivery schedules, and vendor performance, allowing manufacturers to make strategic purchasing decisions.
Data-driven supply chain management reduces excess costs and improves order fulfillment accuracy. With MES, manufacturers can align production schedules with increase in forecasts, minimizing waste and improving efficiency. These capabilities help maintain seamless operations while reducing logistical challenges.
5. Integration with Industrial IoT
Manufacturers are integrating industrial IoT (IIoT) technologies to improve automation, monitoring, and data collection. MES connects with IIoT-enabled devices, allowing production systems to gather performance data from smart sensors, robotics, and connected machinery. This integration improves real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated solutions.
MES analyzes machine-generated data to provide insights into operational efficiency. Manufacturers can track energy consumption, equipment performance, and conditions, ensuring that production parameters remain within optimal ranges. These insights help detect inefficiencies and make data-driven adjustments to improve productivity.
Automated communication between MES and IIoT devices enhances process control. Innovative machinery can adjust production variables in response to MES instructions, improving precision and reducing variability. This level of automation ensures that production remains consistent while minimizing human intervention.
6. Predictive Maintenance
Equipment failures can cause costly production disruptions. MES provides predictive maintenance capabilities by analyzing machine performance data, detecting early warning signs of mechanical issues, and automating maintenance scheduling before breakdowns occur.
Continuous equipment monitoring allows MES to track temperature fluctuations, vibration levels, and operational deviations that indicate potential failures. Automated alerts notify maintenance teams when predefined thresholds are exceeded, allowing them to perform preventive maintenance before the issue escalates.
Optimizing maintenance schedules improves asset longevity and reduces unplanned downtime. Manufacturers can extend the lifespan of machinery, lower repair costs, and prevent unexpected production delays. Predictive maintenance reduces reliance on reactive repair strategies, improving overall equipment efficiency.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers operating in regulated industries must maintain detailed production records to meet industry standards. MES simplifies compliance by automating documentation, tracking material usage, and enforcing process controls that align with regulatory requirements.
Traceability features provide a clear record of product genealogy, allowing manufacturers to trace components and production steps in case of audits or recalls. MES also generates electronic batch records that streamline regulatory reporting, reducing manual documentation efforts.
Industries such as medical devices, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing benefit from MES compliance tools, as these systems provide the documentation needed to verify adherence to quality and safety standards. Automated compliance tracking reduces the risk of nonconformities and improves audit readiness.
Manufacturing execution systems are essential in industrial automation, offering real-time tracking, efficiency improvements, and compliance support. These systems provide the digital infrastructure manufacturers need to manage complex production workflows while maintaining high product quality.
Manufacturers can optimize production processes and reduce operational risks by integrating MES with IIoT, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management. The ability to monitor and control every stage of manufacturing ensures consistent output, lower costs, and improved regulatory compliance. MES continues to be a vital tool for industrial automation, supporting manufacturers in achieving efficiency and reliability across production operations.
Implementing MES in Industrial Automation
Manufacturers rely on MES to improve efficiency, standardize workflows, and enhance production visibility. Successful implementation requires strategic planning, alignment with existing infrastructure, and seamless integration with enterprise systems. MES solutions must support production goals while minimizing disruptions during deployment. Implementation begins with assessing production workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs). Understanding current operational challenges helps manufacturers configure MES to address specific needs, such as reducing downtime, improving quality control, or enhancing supply chain coordination. Establishing clear objectives ensures that MES delivers measurable improvements across production operations.
System integration plays a vital role in MES deployment. MES must connect with ERP, industrial IoT (IIoT) devices, and manufacturing equipment to provide accurate, real-time data. Compatibility with existing hardware and software solutions ensures smooth data exchange, preventing information silos and delays in production monitoring. MES also requires configuration to align with regulatory requirements, providing accurate documentation and traceability in compliance-driven industries.
Training and adoption strategies determine the success of MES implementation. Operators, engineers, and managers must understand how to use MES tools effectively. User-friendly interfaces, automated reporting, and role-based access help teams transition to digital workflows without disruptions. Ongoing support and training ensures employees maximize MES capabilities, improving production efficiency and operational control.
Continuous optimization allows manufacturers to refine MES performance over time. Real-time monitoring and historical data analysis provide insights into production trends, equipment performance, and process bottlenecks. Manufacturers can adjust MES configurations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. As industrial automation advances, MES is a scalable solution that adapts to new manufacturing needs.
Manufacturers worldwide embrace cloud-based solutions to achieve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver smart, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing execution systems (MES) provide real-time visibility into production processes, reducing downtime and optimizing efficiency.
- MES enhances quality control and compliance tracking by automating inspections, documentation, and traceability reporting for regulated industries.
- Resource optimization features in MES reduce costs by improving inventory management, automating scheduling, and minimizing material waste.
- Integrating industrial IoT (IIoT) devices strengthens automation, continuously monitoring machine performance and predictive maintenance alerts.
- MES improves supply chain coordination by synchronizing material tracking, supplier performance, and inventory levels, reducing disruptions in production.
FAQs
MES improves industrial automation by monitoring real-time production, reducing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization. These systems automate data collection, streamline workflows, and support predictive maintenance, ensuring smooth manufacturing operations. MES also enhances compliance tracking and quality control, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
MES is widely used in industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, and consumer electronics. These industries require strict process control, compliance tracking, and efficiency improvements. MES helps manufacturers maintain traceability, manage production schedules, and enhance product quality.
MES focuses on shop floor operations, providing real-time tracking and automation, while ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) handles business-wide functions such as finance, procurement, and logistics. MES integrates with ERP to ensure seamless data exchange between production and business processes, improving overall operational visibility.
MES records detailed production data, including material usage, work instructions, and inspection results, simplifying compliance tracking. These systems generate audit-ready reports, automate traceability, and ensure adherence to industry standards in regulated sectors such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
MES integrates with industrial IoT (IIoT) devices to enhance automation and real-time monitoring. Connected sensors and smart machinery feed data into MES, providing insights into equipment performance, energy consumption, and predictive maintenance needs. This integration improves process control and reduces manual intervention.
Understanding Composability in Manufacturing
Understanding Composability in Manufacturing
Manufacturers must rethink traditional production models to meet shifting needs, integrate emerging technologies, and maintain efficiency.
Rigid, monolithic systems no longer provide the adaptability to optimize workflows and minimize disruptions. Composable manufacturing introduces a modular approach, allowing production lines to be reconfigured quickly without extensive downtime or costly overhauls. Manufacturers can increase agility, reduce operational risks, and scale production capacity by focusing on standardization, interoperability, and automation. Understanding how composable manufacturing works, its key benefits, and its practical applications provides valuable insight into its growing role in modern production.
What is Composability in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing composability refers to the ability to assemble, disassemble, and reconfigure manufacturing processes and systems based on modular, interoperable components. Unlike rigid, monolithic production systems, composable manufacturing equips manufacturers to create highly adaptable production settings that quickly adjust to shifting market needs, new product requirements, and developing supply chain conditions.
This approach relies on standardized, plug-and-play components that can be reconfigured with minimal downtime, allowing for greater agility and efficiency. Manufacturers using composable systems can respond to fluctuations in production volume, introduce new technologies seamlessly, and integrate automation solutions without overhauling existing infrastructure. The result is a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective production model that enhances operational efficiency and reduces time to market.
The Evolution of Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Manufacturing has shifted from rigid, labor-intensive production models to adaptable, technology-driven systems that improve efficiency and scalability. The path toward composable manufacturing builds on key advancements in automation, digitalization, and modular system design. Each stage of this progression has introduced solutions to reduce waste, lower costs, and improve production flexibility.
- Manual Production Lines: Early manufacturing relied entirely on human labor, making production processes slow, costly, and prone to errors. Adjustments to production workflows required extensive retraining and manual retooling, leading to significant downtime and inefficiencies. Despite these challenges, manual systems allowed for high levels of customization, which was difficult to achieve with later automated methods.
- Introduction of Automated Assembly Systems: As industries sought ways to increase output and reduce labor costs, automated machinery became a standard feature of production lines. Mechanized conveyor belts, robotic arms, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) allowed for higher efficiency and consistency. However, early automation systems were rigid, requiring costly modifications when introducing new products or production methods.
- Development of Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS): Recognizing the limitations of static automation, manufacturers introduced flexible manufacturing systems that allowed for faster adjustments. These systems incorporated robotics, computer-controlled machinery, and programmable automation to support multiple product variations on a single production line. Despite offering greater adaptability, FMS often required specialized expertise to configure and maintain, limiting adoption in smaller manufacturing operations.
- Advancements in Smart Manufacturing Technologies: The rise of data-driven production introduced smart sensors, cloud computing, and industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions that enhanced flexibility. Real-time analytics and predictive maintenance tools equip manufacturers to make informed decisions about process improvements, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency. Despite these innovations, manufacturers faced integration challenges when connecting legacy systems with newer digital technologies.
- Adoption of Composable Manufacturing: The shift toward composable manufacturing builds on the strengths of earlier systems while addressing their shortcomings. Modular production components, software-defined automation, and AI-driven optimization allow manufacturers to reconfigure operations with minimal disruption. Unlike traditional automation, which often requires dedicated infrastructure, composable systems support plug-and-play adaptability, making production lines more scalable and cost-effective.
Manufacturers seeking to improve operational efficiency must consider how composability builds on past advancements while addressing the limitations of earlier manufacturing models. Implementing modular systems, digital tools, and flexible automation provides a structured approach to adapting production processes based on market shifts, supply chain variability, and emerging technologies.
Benefits of Composability in Manufacturing
Manufacturing composability allows companies to create highly adaptable production systems that improve efficiency, scalability, and cost control. Traditional manufacturing systems often require significant investments in infrastructure changes to accommodate new products, production methods, or automation technologies. Composable manufacturing eliminates these barriers by enabling manufacturers to reconfigure production lines and integrate new components with minimal disruption. This approach provides several operational advantages that help manufacturers meet shifting requirements while reducing unnecessary costs and downtime.
- Increased Agility in Production Processes: Traditional manufacturing setups are often complex to modify, requiring extensive planning and downtime when adjusting for new products or processes. Composable manufacturing eliminates these bottlenecks by allowing production lines to be reconfigured with modular equipment and software-defined automation. This makes it easier to accommodate shifts in product need, introduce new materials, or adjust workflows without overhauling existing systems.
- Lower Operational and Capital Costs: Replacing entire production lines or investing in new infrastructure can be costly and time-consuming. Composable manufacturing reduces the need for large-scale capital expenditures by allowing manufacturers to repurpose existing equipment and integrate new technologies without significant financial commitments. Lower maintenance costs and improved resource allocation further contribute to long-term cost savings.
- Scalability for Production Volume Adjustments: Manufacturers often need to adjust output based on supply chain conditions, seasonal need, or shifts in consumer preferences. Composable manufacturing allows for incremental scaling, increasing or decreasing production capacity without requiring an entirely new setup. This ensures that manufacturers can remain efficient while avoiding overproduction or supply shortages.
- Faster Integration of New Technologies: Emerging automation solutions, AI-driven analytics, and IoT monitoring systems provide significant advantages, but integrating these technologies into traditional manufacturing settings can be complex and expensive. Composable manufacturing systems use standardized interfaces that simplify adopting new technologies, allowing manufacturers to upgrade processes without costly or time-intensive retrofits.
- Improved Resilience Against Disruptions: Unplanned equipment failures, supply chain shortages, and shifting regulatory requirements can disrupt traditional production systems. Composability minimizes these risks by ensuring that production lines can be quickly reconfigured in response to unexpected challenges. Manufacturers can swap out components, adjust workflows, or reallocate resources to maintain operational continuity.
- Enhanced Product Customization Without Sacrificing Efficiency: Consumers and industries slowly require more personalized and specialized products, yet traditional mass production methods struggle to meet these expectations. Composable manufacturing equips high levels of customization by allowing manufacturers to quickly adapt production lines for different product variations, materials, or specifications without compromising efficiency or increasing costs.
Manufacturers looking to increase efficiency, reduce operational risks, and improve scalability can benefit from composable manufacturing’s modular and adaptable structure. This approach ensures that production systems remain flexible and cost-effective while supporting long-term innovation and operational stability.
Real-World Applications of Composable Manufacturing
Industries with complex production requirements and high variability in product specifications require manufacturing systems that can quickly adapt to new processes, materials, and regulations. Composable manufacturing provides the flexibility to integrate automation, customize production lines, and respond to shifting supply chain conditions. This approach has been widely adopted across industries that require high precision, regulatory compliance, and rapid production adjustments.
Automotive Manufacturing
Automakers must regularly adjust production lines to accommodate new models, alternative powertrains, and shifting consumer preferences. Composable manufacturing allows automotive plants to modify assembly lines with modular robotic systems and flexible tooling, making transitioning between internal combustion engine vehicles and electric vehicle (EV) production easier. Software-driven automation also allows manufacturers to adjust workflows without manual intervention, reducing downtime and improving production efficiency.
Medical Device and Pharmaceutical Production
Strict regulatory requirements in medical device and pharmaceutical manufacturing require high precision and traceability levels. Composable manufacturing allows these industries to reconfigure production lines to meet compliance standards, implement digital quality control systems, and integrate real-time monitoring solutions. This flexibility reduces the time and effort required to adjust for new regulatory updates while ensuring that products meet safety and efficacy standards.
Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing
Aerospace and defense manufacturers require production systems that support high-mix, low-volume production and mass production of standardized components. Composable manufacturing allows switching between custom-built aircraft parts and standardized military components without significant production delays. Digital twins and AI-driven simulations also play a key role in optimizing assembly processes, reducing errors, and minimizing material waste.
Semiconductor and Electronics Production
Semiconductor manufacturing requires highly controlled production conditions and frequent process updates to accommodate next-generation chip designs. Composable manufacturing supports modular cleanroom production systems, allowing manufacturers to reconfigure fabrication processes without shutting down entire facilities. Automation and AI-powered process optimization further enhance efficiency by identifying opportunities for reducing material waste and improving defect detection.
Heavy Machinery and Industrial Equipment Manufacturing
Manufacturers producing industrial equipment, mining machinery, and construction tools need flexible production systems for customization and scalability. Composable manufacturing supports standardized component integration, making it easier to produce different product configurations while maintaining high levels of efficiency. Modifying production lines for new equipment models without investing in entirely new infrastructure reduces costs and improves long-term production flexibility.
Industries adopting composable manufacturing benefit from reduced production downtime, improved cost control, and the ability to integrate advanced automation solutions. This approach ensures that manufacturing systems remain adaptable, scalable, and efficient without costly infrastructure overhauls.
Implementing Composability in Manufacturing
Manufacturers seeking composable manufacturing must focus on system interoperability, modular equipment design, and data-driven automation. A structured implementation approach ensures that production systems remain flexible while minimizing disruptions.
Modular Equipment and Standardized Interfaces
Manufacturing systems built with interchangeable components allow for easier reconfiguration when production requirements shift. Standardized machine interfaces ensure that equipment from different vendors can work, eliminating compatibility issues that often delay integration. Modular design also reduces the need for custom-built solutions, lowering costs and improving scalability.
Digital Twin Technology for Process Optimization
Digital twins provide virtual simulations of production workflows, allowing manufacturers to test new configurations before making physical adjustments. This technology improves control by identifying potential bottlenecks, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring that production changes do not introduce inefficiencies. Manufacturers using digital twins can confidently implement process modifications, reducing trial-and-error disruptions.
AI-Driven Automation and Robotics Integration
Automation plays a critical role in composable manufacturing by allowing production lines to adapt to shifting requirements with minimal manual intervention. AI-powered robotics and process control systems adjust workflows based on real-time data, improving efficiency and reducing waste. Collaborative robots (cobots) further enhance flexibility by assisting with assembly tasks that require human-machine interaction.
Data Standardization and Industrial IoT Connectivity
Seamless communication between production systems ensures that composable manufacturing functions as a unified operation. Standardized communication protocols such as OPC UA and MQTT allow data to flow securely between machines, sensors, and cloud-based analytics platforms. Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance systems help manufacturers prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving overall equipment effectiveness.
Supply Chain Integration and Vendor Collaboration
Manufacturers implementing composable systems must work closely with suppliers that support modular component compatibility. Selecting technology providers prioritizing interoperability ensures that new equipment and software solutions integrate smoothly. This approach minimizes disruptions when introducing new materials, automation systems, or production line modifications.
A structured approach to implementing composable manufacturing allows companies to optimize efficiency, integrate emerging technologies, and adjust production processes without significant disruptions. This adaptability ensures manufacturers meet shifting production requirements while improving cost control and resource utilization.
Future of Composability in Manufacturing
Manufacturers are expected to increase their adoption of composable manufacturing as the industry needs to shift toward greater flexibility, automation, and sustainability. Modular production systems will play a key role in meeting these needs while minimizing operational disruptions.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will refine composable manufacturing by automating real-time process adjustments and predictive maintenance. Advanced analytics will equip manufacturers to optimize production schedules, reduce waste, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Cloud-based platforms will also enhance system interoperability, seamlessly integrating new technologies without costly infrastructure overhauls.
Sustainability will remain a priority, with composable manufacturing supporting energy-efficient production methods and waste reduction. The ability to reconfigure production lines based on material availability and regulatory requirements will help manufacturers lower costs while meeting goals.
Adopting composable manufacturing will become an industry standard as companies seek to improve agility, reduce operational risks, and integrate advanced technologies into their production workflows.
Manufacturers worldwide embrace cloud-based solutions to achieve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver innovative, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Composable manufacturing enhances production flexibility by enabling quick system modifications without requiring significant downtime or reconfiguration.
- Modular components and standardized interfaces simplify integration, allowing manufacturers to incorporate automation, robotics, and AI-driven analytics efficiently.
- Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and semiconductor manufacturing benefit significantly from composable manufacturing due to its scalability and adaptability.
- Data-driven automation and digital twins improve production efficiency, allowing manufacturers to simulate, test, and optimize workflow adjustments in real time.
- Cost savings result from reduced infrastructure investment, lower maintenance requirements, and the ability to adapt existing production systems without complete replacements.
FAQs
Manufacturing composability refers to the ability to configure, adjust, and optimize production systems using modular, interoperable components. This approach allows manufacturers to reconfigure workflows, integrate automation, and adapt to supply chain variability with minimal disruption. The result is a more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective production model.
Composable manufacturing improves efficiency by allowing manufacturers to quickly adjust production lines without costly retooling. Modular systems reduce downtime, optimize resource allocation, and integrate seamlessly with automation and AI-driven monitoring. This adaptability ensures continuous production flow, even during disruptions or product design changes.
Industries requiring high precision, scalability, and customization benefit the most from composable manufacturing. Automotive, aerospace, medical device, semiconductor, and industrial equipment manufacturers use this approach to optimize production while meeting strict regulatory and quality requirements. The ability to modify workflows without major overhauls makes it ideal for industries with frequently shifting needs.
Composable manufacturing supports automation using standardized interfaces that integrate seamlessly with robotic systems and AI-driven process controls. This approach automated adjustments in workflow configuration, material handling, and real-time monitoring. Manufacturers can implement collaborative robots (cobots) and AI-driven analytics without disrupting operations.
The modular nature of composable manufacturing reduces capital expenditures by eliminating the need for large-scale infrastructure changes. Manufacturers can repurpose existing equipment, integrate new technologies incrementally, and reduce waste associated with inefficiencies. Lower maintenance costs and improved adaptability contribute to long-term financial savings.
How MES Supports Medical Device Manufacturing
How MES Supports Medical Device Manufacturing
Manufacturing medical devices require absolute precision, strict compliance, and streamlined production processes.
Every stage, from raw material sourcing to final product assembly, must meet regulatory standards while maintaining efficiency and traceability. Errors in production can lead to costly recalls, regulatory violations, and compromised patient safety. As manufacturers work to balance quality control, cost management, and operational efficiency, technology plays a critical role in modernizing workflows.
A manufacturing execution system (MES) improves medical device manufacturing by optimizing production control, ensuring compliance, and enhancing traceability. With real-time monitoring, automated workflows, and seamless system integration, MES helps manufacturers meet the industry's highest standards while reducing inefficiencies. As regulatory requirements grow more complex and supply chains face ongoing disruptions, manufacturers must adopt digital solutions to maintain accuracy and productivity.
What is Medical Device Manufacturing?
Medical device manufacturing is designing, producing, testing, and distributing medical equipment used to diagnose, treat, monitor, and prevent diseases. This industry covers various products, including surgical instruments, imaging systems, implants, diagnostic devices, and wearable health monitors. Each product must meet stringent regulatory safety, accuracy, and reliability requirements.
Manufacturers operate under strict quality control systems due to the high-stakes nature of healthcare. Regulations such as those set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and international standards like ISO 13485 outline precise criteria for design validation, process control, and documentation. As a result, companies in this sector require robust manufacturing execution systems (MES) to maintain efficiency, traceability, and compliance while meeting production requests.
Role of MES in Medical Device Manufacturing
A manufacturing execution system (MES) is essential in medical device manufacturing as it improves production efficiency, enforces process controls, and ensures product traceability. This technology bridges the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and shop floor operations, providing real-time data on production workflows, equipment status, and quality metrics.
Regulatory compliance remains a significant challenge in medical manufacturing, and MES helps streamline data collection, electronic batch records, and audit trails. Automated workflows reduce the risk of human error while supporting strict documentation requirements. MES also integrates with quality management systems to track deviations, defects, and corrective actions, improving overall product consistency.
Advanced MES solutions support manufacturing optimization by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle times, machine utilization, and yield rates. Manufacturers gain insights into production bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing them to refine processes and improve throughput while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Benefits of MES in Medical Device Manufacturing
"MES enhances regulatory compliance, automates data collection, and improves production efficiency. It reduces human errors, enforces standardized workflows, and integrates with enterprise systems for seamless data sharing."
Medical device manufacturing requires high precision, compliance, and efficiency. Every step of the production process must meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining cost control and product quality. A manufacturing execution system (MES) addresses these challenges by improving traceability, automating workflows, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. The ability to capture real-time data, enforce process controls, and integrate with other enterprise systems makes MES an essential tool for manufacturers looking to improve compliance and productivity while reducing risks.
- Regulatory Compliance Support: Meeting FDA, ISO 13485, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) requirements requires strict documentation, audit readiness, and validation. MES automates record-keeping, ensuring that all production data, process deviations, and quality checks are documented in real-time. This significantly reduces the risk of non-compliance while simplifying regulatory reporting and inspections.
- Complete Product Traceability: Manufacturing medical devices require detailed tracking of every component and material used in production. MES provides complete product genealogy, capturing serial numbers, lot numbers, and material sources from raw materials to finished products. This level of traceability enhances recall management, allowing manufacturers to quickly isolate and address defective batches, minimizing patient risk and regulatory consequences.
- Error Reduction and Process Standardization: Human errors in medical manufacturing can lead to serious safety concerns and regulatory violations. MES enforces standardized operating procedures (SOPs), ensuring operators follow defined assembly, testing, and inspection workflows. Digital work instructions guide workers through each process step, reducing variability and minimizing mistakes that could compromise product quality.
- Production Efficiency and Resource Optimization: Optimizing manufacturing workflows requires real-time visibility into production status, machine utilization, and labor efficiency. MES provides live data on work-in-progress (WIP), cycle times, and equipment performance, helping manufacturers identify bottlenecks and improve overall throughput. This reduces downtime, increases yield rates, and maximizes resource utilization. Automated Quality Control and Defect Management: Quality assurance in medical device manufacturing requires proactive defect detection and corrective action tracking. MES integrates with quality management systems (QMS) to capture inspection results, detect process deviations, and enforce corrective actions. Real-time monitoring helps manufacturers address quality concerns before they escalate, reducing waste and rework costs.
- Shorter Time-to-Market for New Products: Bringing a new medical device to market requires extensive testing, documentation, and validation before regulatory approval. MES accelerates this process by centralizing production data, automating batch record creation, and streamlining validation procedures. Faster access to real-time data allows manufacturers to make informed adjustments and ensure compliance without delaying product launches.
- Cost Reduction Through Waste Minimization: Material waste, excessive rework, and unplanned downtime can significantly impact production costs. MES improves inventory tracking, prevents overuse of materials, and provides insights into waste reduction opportunities. Manufacturers can lower production costs by minimizing defects, rework, and inefficiencies while maintaining high-quality standards.
- Seamless Integration with Enterprise Systems: Medical manufacturers often use multiple systems, including enterprise resource planning (ERP), product lifecycle management (PLM), and warehouse management solutions. MES is a central hub connecting these systems, ensuring data consistency across departments. This integration improves communication between design, production, and supply chain teams, improving coordination and efficiency.
Implementing MES in medical device manufacturing enhances operational efficiency, reduces compliance risks, and improves product quality. With advanced process control, real-time monitoring, and seamless data integration, manufacturers can streamline their operations while maintaining the highest safety and reliability standards.
Key Features of MES for Medical Devices
Medical device manufacturing requires precision, compliance, and real-time visibility into production processes. A manufacturing execution system (MES) provides the necessary tools to maintain strict quality standards while improving efficiency across every production stage. The ability to track materials, enforce process control, and integrate with enterprise systems ensures that manufacturers can meet regulatory requirements while optimizing operations. Key MES features designed for medical manufacturing improve traceability, automate data collection, and enhance production reliability.
Electronic Batch Records (EBR) for Compliance and Documentation
Maintaining accurate and complete batch records is critical for medical device manufacturing. MES replaces manual documentation with electronic batch records (EBR), ensuring that every step of production is automatically logged in a secure and audit-ready format. These records capture operator actions, machine settings, material usage, and process deviations, reducing the risk of human error and compliance violations. Automated record-keeping simplifies regulatory reporting, providing manufacturers faster access to production data during inspections or audits.
End-to-end traceability and Genealogy Tracking
Full product traceability is essential for medical devices, where even minor defects can have serious consequences. MES provides detailed genealogy tracking, recording every component and material used in production. Serial numbers and lot tracking allow manufacturers to trace individual devices to their source materials, suppliers, and production batches. In the event of a recall or compliance review, MES authorize quick identification of affected products, minimizing risk and improving response times.
Process and Quality Control Enforcement
Manufacturing medical devices require adherence to strict process control measures. MES enforces standard operating procedures (SOPs) by guiding operators through predefined workflows, preventing deviations that could impact quality. Integration with quality management systems (QMS) allows MES to capture real-time inspection results, flag defects, and trigger corrective actions. Automated quality control ensures that defective products are identified before distribution, reducing waste and preventing costly rework.
Real-Time Production Monitoring and Performance Analytics
Real-time visibility into production processes allows manufacturers to make informed decisions and improve operational efficiency. MES provides live tracking of work-in-progress (WIP), machine performance, and operator productivity. Data-driven insights help identify bottlenecks, optimize cycle times, and improve resource allocation. Dashboards and automated alerts provide instant updates on critical production metrics, allowing manufacturers to address inefficiencies before they impact output.
Digital Work Instructions and Operator Guidance
Medical device manufacturing involves complex assembly and testing procedures that require precision. MES provides digital work instructions that guide operators through each production step, ensuring consistency and reducing training time for new workers. Instructions can be updated in real time to reflect process changes or regulatory updates, ensuring that employees always follow the latest approved procedures. Visual aids, interactive checklists, and automated validation steps help reduce human errors and improve overall production accuracy.
Regulatory Compliance Management with Secure Data Logging
Compliance with FDA regulations, ISO 13485, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) requires detailed record-keeping and controlled workflows. MES ensures compliance by automating data collection, securing electronic signatures, and maintaining audit trails. Secure data logging prevents unauthorized changes to production records, reducing the risk of compliance violations. Electronic records simplify audit preparation, allowing manufacturers to retrieve necessary documentation quickly and accurately.
Seamless Integration with ERP and PLM Systems
Medical manufacturers rely on multiple enterprise systems, including enterprise resource planning (ERP) and product lifecycle management (PLM). MES bridges these systems, ensuring seamless data flow between design, production, and supply chain operations. Real-time integration improves material planning, reduces delays, and ensures production aligns with forecasts. Synchronizing MES with ERP and PLM enhances overall efficiency and eliminates data silos.
Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Efficiency Monitoring
Unplanned equipment failures can lead to costly downtime and production delays. MES collects machine performance data, tracks usage patterns, and identifies potential failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance scheduling ensures equipment is serviced at optimal intervals, reducing unexpected breakdowns. Monitoring machine efficiency also helps manufacturers maximize production capacity while minimizing maintenance costs.
These key MES features provide medical device manufacturers with the tools to maintain regulatory compliance, improve product quality, and optimize production efficiency. Automating critical processes and ensuring real-time visibility allows companies to reduce risks, control costs, and meet the highest industry standards for precision and reliability.
Applications of MES in Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturing requires strict control over production processes, compliance management, and quality assurance. A manufacturing execution system (MES) plays a vital role in optimizing operations, improving traceability, and ensuring real-time visibility into every stage of production. The ability to automate workflows, enforce regulatory requirements, and integrate with other enterprise systems makes MES a valuable asset for manufacturers looking to improve efficiency while maintaining compliance.
Production Process Control and Standardization
Medical device manufacturing involves complex workflows that must adhere to strict regulatory standards. MES enforces production consistency by standardizing processes, ensuring that each step follows predefined specifications. Automated workflow controls prevent unauthorized process deviations, reducing the risk of human errors and production defects. MES also tracks and validates each step-in real time, providing instant verification that all manufacturing activities meet established quality standards.
Material and Inventory Management for Accuracy and Efficiency
Raw materials and components used in medical device production must be precisely tracked to ensure compliance and product integrity. MES provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, reducing waste and preventing shortages that could disrupt production. Advanced tracking capabilities allow manufacturers to manage lot numbers, expiration dates, and supplier information, ensuring that only approved materials are used in production. Automated inventory updates improve material planning and reduce excess stock, optimizing warehouse efficiency.
Quality Assurance and Regulatory Compliance Enforcement
Ensuring that medical devices meet regulatory requirements is a top priority for manufacturers. MES integrates with quality management systems (QMS) to automate quality checks, inspection results, and deviation tracking. Real-time data collection allows for immediate detection of defects, triggering corrective actions before faulty products reach the market. Compliance enforcement features like electronic batch records (EBR), and digital signatures help manufacturers maintain audit-ready documentation while simplifying regulatory reporting.
Product Traceability and Recall Management
A strong traceability system is essential in medical manufacturing to track the entire lifecycle of a product. MES captures detailed genealogy data, recording every material, component, and process step involved in device production. Serial number and lot tracking provide complete visibility into each product’s history, ensuring rapid identification of affected devices in case of a recall. Automated traceability functions improve recall readiness, helping manufacturers respond quickly while minimizing patient risk and regulatory penalties.
Equipment Performance Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Unplanned equipment failures can disrupt production schedules and increase costs. MES collects real-time machine performance data, tracking usage patterns to predict potential failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance scheduling reduces unplanned downtime by servicing machines at optimal intervals. Monitoring equipment efficiency also helps manufacturers extend asset lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and improve production reliability.
Operator Training and Certification Management
Medical device manufacturing requires skilled operators trained in industry regulations, safety standards, and process-specific tasks. MES tracks operator certifications, ensuring only qualified personnel perform critical manufacturing activities. Automated alerts notify managers when certifications are due for renewal, preventing compliance issues related to unqualified labor. Digital work instructions and real-time guidance further support operator training, reducing onboarding time and improving accuracy in production tasks.
These MES applications improve medical device manufacturing by enhancing process control, improving compliance readiness, and reducing production inefficiencies. Automating data collection, enforcing quality standards, and providing real-time production insights allow manufacturers to maintain high product quality while optimizing operational costs.
Challenges in Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturing presents unique challenges due to strict regulatory requirements, complex production processes, and the need for absolute precision. Every product must meet rigorous safety and quality standards while maintaining efficiency in manufacturing operations. Companies in this sector must balance compliance, cost control, and product innovation while addressing ongoing industry challenges.
- Regulatory Compliance Complexity: Meeting FDA, ISO 13485, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards requires extensive documentation, validation, and audits. Regulatory agencies impose strict guidelines on production processes, material traceability, and product testing. Failure to adhere to these requirements can result in costly delays, product recalls, or legal penalties.
- Supply Chain Disruptions and Material Sourcing Issues: Medical devices rely on specialized components and high-quality raw materials, which must meet strict regulatory and performance standards. Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical factors, and shortages of critical materials can slow production and increase costs. Manufacturers must develop contingency plans, establish reliable supplier networks, and implement real-time inventory tracking to minimize risks.
- Stringent Quality Control and Risk Management: Every medical device must be manufactured to exact specifications, leaving no room for errors or defects. Strict quality control measures must be enforced to detect potential deviations before products reach the market. Automated inspection systems, real-time monitoring, and corrective action tracking are essential for ensuring product reliability and patient safety.
- High Production Costs and Cost Control Pressures: Developing and manufacturing medical devices requires substantial investment in research, materials, equipment, and regulatory compliance. Production costs can rise due to material waste, inefficient workflows, and labor-intensive processes. Optimizing manufacturing efficiency through automation, MES integration, and predictive analytics helps companies maintain cost control without compromising quality.
- Product Traceability and Recall Preparedness: Medical device manufacturers must maintain complete traceability of all components and production processes. In case of a defect or safety concern, companies must quickly identify and recall affected products to minimize patient risk. MES solutions provide real-time tracking and batch genealogy, allowing manufacturers to trace products back to their source and take corrective action immediately.
- Workforce Training and Certification Management: Manufacturing medical devices requires a highly trained workforce understanding complex assembly processes and regulatory requirements. Keeping employees up to date with certifications, process changes, and safety protocols is essential to maintaining compliance. MES solutions help track training records, ensuring that only qualified personnel perform specific tasks.
- Spread Technological and Regulatory View: New medical technologies, advanced manufacturing techniques, and updated regulatory frameworks require companies to adapt continuously. Staying ahead of industry changes while maintaining compliance and production efficiency requires ongoing investment in research, process improvements, and workforce training.
Medical device manufacturers must these challenges while maintaining quality, compliance, and efficiency. Implementing an MES helps companies address these concerns by improving production visibility, automating compliance tasks, and optimizing manufacturing workflows.
Understanding Medical Device Manufacturing Costs
Medical device manufacturing involves substantial costs due to regulatory compliance, material sourcing, labor, and technology investments. Companies must carefully manage these expenses to maintain profitability while ensuring product quality and safety.
Regulatory requirements contribute significantly to manufacturing costs. Compliance with FDA standards, ISO 13485, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) require extensive documentation, process validation, and ongoing quality assurance. Failure to meet these regulations can lead to costly rework, fines, or product recalls. Investing in an MES helps manufacturers streamline compliance efforts, reducing manual labor and documentation errors.
Material and equipment expenses also affect overall costs. High-grade materials, such as biocompatible metals and medical-grade polymers, are essential for device performance and patient safety. Precision manufacturing equipment, cleanroom facilities, and automation systems increase capital expenditures. Implementing MES allows manufacturers to optimize material usage, track inventory in real-time, and reduce waste, leading to cost savings.
Labor costs remain a key factor in medical device production. Skilled technicians, engineers, and quality control personnel must ensure that products meet strict standards. MES helps improve workforce efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, providing digital work instructions, and tracking operator performance. Reducing manual interventions lowers labor costs and minimizes human errors.
Managing these cost factors effectively requires data-driven and process optimization. MES provides real-time insights into production efficiency, resource utilization, and waste reduction, allowing manufacturers to control expenses while maintaining high product standards.
Emerging Trends in MES and Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturing continues progressing as new technologies and process innovations improve efficiency, compliance, and production quality. Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are advancing to meet these requests, incorporating automation, data-driven insights, and enhanced connectivity. These trends shape how manufacturers produce, monitor, and manage medical devices, allowing for greater precision, lower costs, and improved regulatory adherence.
- AI-Powered Analytics and Predictive Quality Control: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being integrated into MES to analyze production data, detect defects, and predict potential failures before they occur. AI-powered insights help manufacturers proactively improve quality control, reduce rework, and optimize production efficiency by identifying patterns that human operators may miss.
- Cloud-Based MES for Scalable Operations: Cloud-based MES solutions provide manufacturers with real-time access to production data across multiple facilities, better coordination and faster response times. Cloud integration reduces the need for on-premises IT infrastructure, making MES deployment more cost-effective while ensuring secure, centralized data storage and remote accessibility.
- Digital Twins for Process Optimization: Digital twin technology is used in medical device manufacturing to create virtual replicas of production. These digital models allow manufacturers to simulate, test, and refine production processes before implementation. Using MES-driven digital twins helps companies optimize workflows, improve product design, and minimize costly trial-and-error adjustments on the shop floor.
- IoT Smart Manufacturing for Real-Time Monitoring: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors enhance MES capabilities by providing continuous real-time data on equipment performance, and production metrics. These connected devices help manufacturers detect inefficiencies, schedule predictive maintenance, and ensure process parameters remain within strict regulatory limits.
- Paperless Manufacturing and Automated Documentation Compliance: The transition to fully digital manufacturing processes eliminates paper-based documentation, reduces errors, and improves compliance. MES solutions automate electronic batch records (EBR), digital work instructions, and real-time data collection, ensuring manufacturers maintain audit-ready documentation without relying on manual record-keeping.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements for Data Protection: As MES platforms become more connected through cloud computing and IoT integration, cybersecurity measures are strengthening to protect sensitive manufacturing and patient-related data. Advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with industry security frameworks help safeguard MES systems from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Advanced Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing: Integrating robotics with MES improves production accuracy and reduces manual labor requirements in medical device manufacturing. Automated assembly lines, robotic-assisted inspections, and AI-driven automation are increasing throughput while maintaining stringent quality control standards. MES synchronizes with these automation technologies to track performance, optimize workflows, and ensure compliance.
These emerging MES trends reshape medical device manufacturing by improving operational visibility, reducing waste, and increasing efficiency. As technology advances, manufacturers that adopt these innovations will be better equipped to manage compliance, reduce costs, and enhance overall production performance.
Manufacturers worldwide embrace cloud-based solutions to achieve efficiency, precision, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver innovative, connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital transformation. Discover how our solutions can empower your factory to achieve its full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Regulatory compliance is a significant challenge in medical device manufacturing, requiring strict documentation, process validation, and traceability. MES automates these processes, reducing errors and ensuring audit-ready records.
- Traceability plays a critical role in medical manufacturing by tracking components, materials, and production history. MES improves recall readiness and enhances product quality by providing complete genealogy tracking.
- Production efficiency is optimized through MES by enforcing standard operating procedures, reducing downtime, and monitoring equipment performance in real time. Manufacturers can improve output while maintaining precision.
- Medical device manufacturers face challenges such as supply chain disruptions, high production costs, and workforce training requirements. MES addresses these concerns by automating workflows, improving resource planning, and supporting operator certification management.
- Emerging trends in MES include AI-driven analytics, cloud-based solutions, and IoT smart manufacturing. These innovations improve quality control, enhance process automation, and provide real-time production insights.
FAQs
Medical device manufacturing involves designing, producing, and testing medical equipment used for diagnosis, treatment, and patient monitoring. Regulations such as FDA requirements and ISO 13485 ensure that these devices meet strict safety, quality, and reliability standards. Compliance with these regulations minimizes the risk of defective products that could harm patients or lead to costly recalls.
An MES tracks materials, components, and production processes in real time, ensuring complete product genealogy. This traceability allows manufacturers to quickly identify and isolate defective batches, making recall management more efficient. By capturing serial numbers, lot data, and operator actions, MES provides a transparent record of every step-in manufacturing.
MES enhances regulatory compliance, automates data collection, and improves production efficiency. It reduces human errors, enforces standardized workflows, and integrates with enterprise systems for seamless data sharing. These capabilities help manufacturers control costs, increase product quality, and accelerate time-to-market for new medical devices.
MES minimizes waste, optimizes resource allocation, and prevents production inefficiencies. Automated tracking of inventory and materials reduces excess stock and prevents shortages that lead to production delays. By improving machine utilization and reducing rework, MES helps manufacturers lower operational costs while maintaining high standards.
Advancements such as AI-powered analytics, cloud-based MES, and IoT smart manufacturing are growing medical device production. Predictive maintenance, digital twins, and automated documentation compliance enhance efficiency and reduce downtime. As cybersecurity improves, manufacturers can securely adopt these innovations while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
13 Benefits of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)

13 Benefits of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
A CMMS eliminates the inefficiencies of manual maintenance tracking, ensuring that equipment remains reliable, costs stay controlled, and operational disruptions are minimized.
Due to disorganized scheduling, businesses that rely on outdated maintenance methods often face unexpected breakdowns, high repair expenses, and lost productivity. A structured approach to maintenance improves efficiency, extends asset lifespan, and enhances decision-making.
Implementing a CMMS helps businesses optimize work order management, track asset performance in real time, and reduce maintenance-related administrative burdens. With a centralized platform that automates preventive maintenance and streamlines reporting, organizations can achieve greater control over maintenance processes while reducing downtime and operational costs.
What is a CMMS?
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software solution designed to streamline and automate maintenance operations across industries. It provides a centralized platform for scheduling, tracking, and managing maintenance tasks, ensuring that assets and equipment remain in optimal working condition. CMMS software replaces traditional paper-based maintenance tracking with a digital system, allowing real-time monitoring, work order management, and historical data analysis.
By implementing a CMMS, organizations gain better control over preventive maintenance, reducing equipment failures and unplanned downtime. The system stores comprehensive asset records, tracks work orders, manages inventory, and provides analytics to improve decision-making. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, facility management, and transportation rely on CMMS to enhance operational efficiency, extend equipment life, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Why CMMS is Important
Effective maintenance management directly affects operational efficiency, cost savings, and asset longevity. A CMMS eliminates the inefficiencies of manual tracking, helping businesses organize maintenance tasks, reduce downtime, and ensure equipment reliability. Without a structured system, unplanned failures lead to production delays, unexpected repair costs, and unnecessary administrative work.
A well-implemented CMMS provides a centralized database that keeps track of maintenance schedules, work orders, asset history, and inventory. This level of organization helps reduce errors, prevent missed maintenance, and improve compliance with safety regulations. Businesses that invest in a CMMS gain greater visibility into asset performance, making it easier to allocate resources, plan preventive maintenance, and extend the useful life of critical equipment.
13 Benefits of CMMS
A CMMS provides structured maintenance management, ensuring that assets remain in peak condition while minimizing operational disruptions. Organizations that rely on outdated tracking methods face unnecessary downtime, excessive repair costs, and inefficient scheduling. A well-implemented CMMS centralizes asset data, optimizes work orders, and automates maintenance planning to improve efficiency.
1: Organized Maintenance Scheduling
Unplanned maintenance leads to unexpected downtime, costly repairs, and inefficient resource allocation. A CMMS eliminates these risks by automating preventive maintenance schedules, ensuring critical equipment receives servicing at the proper intervals.
Automated scheduling reduces the reliance on manual tracking, preventing missed inspections that could lead to mechanical failures. Maintenance teams receive real-time alerts for upcoming tasks, allowing them to allocate resources efficiently and avoid last-minute disruptions. Standardizing maintenance timelines improves asset reliability and extends equipment lifespan, ultimately lowering operational costs.
2: Access to Asset Information in Real Time
Maintenance decisions require accurate and immediate asset data. A CMMS provides instant access to equipment specifications, maintenance history, warranty details, and real-time performance updates, eliminating the inefficiencies of manual record-keeping.
Technicians no longer need to search paper logs or spreadsheets to retrieve asset information. With digital access to comprehensive records, they can diagnose issues faster, perform timely maintenance, and reduce unnecessary downtime. Having real-time visibility into asset conditions improves response times and enhances operational efficiency.
3: Superior Work Order and Request Management Capabilities
Manual work order management leads to miscommunication, scheduling conflicts, and delays in task completion. A CMMS streamlines this process by automating work order creation, assignment, and tracking, ensuring that maintenance requests are processed efficiently.
Technicians receive detailed instructions, priority levels, and asset histories within the system, eliminating confusion and reducing response times. Digital tracking improves accountability by providing clear timelines and completion records. Efficient work order management enhances team coordination, leading to faster repairs and optimized resource allocation.
4: Streamlined Tracking of Cost and Purchase Orders
Uncontrolled maintenance expenses and inefficient purchasing processes lead to unnecessary spending. A CMMS records all maintenance-related costs, tracks purchase orders, and provides visibility into spending trends.
With accurate cost tracking, organizations can identify budget overruns, analyze repair versus replacement costs, and forecast future expenses. The system ensures that spare parts are reordered before stock levels become critically low, preventing equipment downtime due to unavailable components. A structured financial approach to maintenance leads to better cost control and improved financial planning.
5: Less Administrative Hassle
Managing maintenance operations with paper-based systems or spreadsheets increases administrative workload, leading to data entry errors and inefficient reporting. A CMMS reduces these burdens by automating routine administrative tasks, allowing maintenance staff to focus on operational priorities.
Automated record-keeping simplifies compliance documentation, work order processing, and asset tracking. Instead of manually logging repairs and inventory updates, technicians input data directly into the system, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Reducing administrative tasks increases productivity and allows maintenance teams to concentrate on keeping equipment in optimal condition.
6: Simplified Record-Keeping
Accurate record-keeping is essential for compliance, audits, and long-term asset management. A CMMS maintains a comprehensive history of all maintenance activities, including repairs, inspections, and part replacements, ensuring that data is readily available when needed.
Digitized records eliminate the risk of lost paperwork and inconsistencies in maintenance logs. Businesses can track asset performance over time, identifying patterns that help refine maintenance strategies. Well-organized documentation supports regulatory compliance and improves planning for future maintenance needs.
7: Reduced Downtime
Unscheduled downtime disrupts operations, reduces productivity, and increases costs. A CMMS minimizes downtime by optimizing maintenance schedules, detecting issues before failures occur, and ensuring that necessary repairs are completed on time.
Preventive maintenance strategies keep equipment running smoothly, reducing the likelihood of sudden breakdowns. When repairs are required, the system prioritizes urgent work orders and ensures that technicians have access to asset histories, streamlining the repair process. Improved maintenance planning keeps production schedules on track and prevents revenue losses caused by unexpected outages.
8: Increased Equipment Longevity
Equipment failure often results from inadequate maintenance or delayed servicing. A CMMS prevents premature wear by enforcing structured maintenance plans based on manufacturer recommendations and operational usage.
Regular servicing reduces the strain on machinery, preventing minor issues from escalating into significant failures. Tracking asset conditions and scheduling timely inspections help businesses extend the lifespan of critical equipment. Longer-lasting assets reduce capital expenditures, lowering the frequency of costly replacements and improving overall return on investment.
9: Reduced Maintenance Backlog
A growing maintenance backlog results in delayed repairs, asset inefficiencies, and increased downtime. A CMMS prevents this by automating work order prioritization, ensuring that urgent tasks are completed without unnecessary delays.
Maintenance teams gain visibility into pending tasks, allowing them to manage workloads effectively. Preventive maintenance reduces the accumulation of overdue repairs, ensuring that equipment remains operational. Keeping maintenance schedules organized improves productivity and prevents disruptions caused by neglected servicing.
10: Streamlined Reporting
Maintenance data is only valuable when it leads to actionable insights. A CMMS generates detailed reports on work order completion rates, asset performance, and cost tracking, helping organizations refine their maintenance strategies.
Comprehensive reporting highlights inefficiencies, identifies recurring equipment issues, and supports budget planning. Decision-makers gain a clear understanding of maintenance trends, allowing them to allocate resources effectively. Data-driven insights improve long-term planning and help businesses optimize maintenance operations.
11: Accessibility to Historic Data
Analyzing past maintenance records provides valuable insights into asset performance and servicing patterns. CMMS stores complete maintenance histories, allowing organizations to track repairs, part replacements, and operational trends.
Having access to detailed records simplifies troubleshooting, as technicians can reference past issues to diagnose current problems. Historical data also helps organizations determine the most effective maintenance schedules, improving efficiency and reducing repair costs. Well-documented records support better long-term asset management and operational planning.
12: Improved Team Communication
Effective communication between maintenance teams, technicians, and management ensures that work orders are processed efficiently and equipment servicing remains on schedule. A CMMS provides a centralized platform for tracking task status, sharing updates, and coordinating responsibilities.
Technicians receive real-time updates on task assignments, reducing the risk of duplicated efforts or miscommunication-related delays. Managers can monitor maintenance progress, ensuring that high-priority tasks receive immediate attention. Strengthened communication improves workflow efficiency and enhances overall team coordination.
13: Enhanced Employee Morale
A structured maintenance system benefits not only equipment performance but also workforce efficiency. A CMMS reduces frustration caused by unclear work orders, last-minute emergency repairs, and inefficient task management.
Technicians operate more effectively when they have precise maintenance schedules, access to asset histories, and well-defined responsibilities. Reducing unplanned repairs and administrative workload improves job satisfaction, creating a more productive work environment. A well-organized system increases morale and enhances overall operational efficiency.
A CMMS offers measurable benefits that improve maintenance effectiveness, extend asset longevity, and optimize operational costs. Organizations that invest in structured maintenance management gain better visibility into equipment performance, reduce unexpected failures, and improve overall productivity.
Financial Benefits of CMMS
A well-implemented CMMS directly impacts financial performance by reducing maintenance costs, optimizing resource allocation, and extending asset life. Businesses that rely on outdated maintenance tracking methods often face excessive repair expenses, unplanned downtime, and inefficient labor management. Implementing a structured maintenance system improves cost control and increases operational efficiency.
A CMMS reduces maintenance expenses by automating preventive maintenance schedules, minimizing emergency repairs, and improving inventory management. Tracking asset performance and maintenance history helps identify cost-saving opportunities, such as reducing over-maintenance or strategically planning equipment replacements. Improved work order management reduces labor inefficiencies, ensuring maintenance teams complete tasks efficiently without unnecessary delays.
Long-term cost savings come from increased equipment longevity and reduced downtime. Keeping assets in peak condition prevents expensive breakdowns and lowers capital expenditures on premature replacements. A CMMS provides data-driven insights that help businesses plan maintenance budgets effectively, reducing unexpected expenses and improving overall financial stability.
Best Practices for Implementing CMMS Systems
A successful CMMS implementation requires careful planning and execution to maximize its benefits. Poor setup and inadequate training often lead to underutilization, which requires following best practices to ensure a smooth transition and long-term success.
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish goals for the CMMS, such as reducing downtime, improving work order efficiency, or lowering maintenance costs. Clear objectives guide system configuration and ensure alignment with business needs.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage maintenance teams, IT personnel, and management early in the process. Their input helps customize the system to match operational requirements and ensures widespread adoption.
- Conduct a Comprehensive Asset Inventory: Gather detailed asset data, including maintenance history, specifications, and manufacturer recommendations. Accurate records improve scheduling and asset management.
- Standardize Workflows and Processes: Establish consistent work order management, preventive maintenance, and inventory tracking procedures. Standardization enhances efficiency and minimizes confusion.
- Provide Adequate Training: Ensure technicians, supervisors, and administrators receive thorough training on system functionality. Well-trained users maximize the CMMS’s potential and prevent misuse.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Verify that asset details, maintenance schedules, and historical records are correct before migration. Inaccurate data leads to inefficiencies and unreliable reporting.
- Set Up Automated Alerts and Notifications: Configure automated reminders for preventive maintenance, overdue work orders, and inventory restocking. These alerts help maintenance teams stay proactive.
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track essential metrics such as work order completion rates, downtime reduction, and maintenance costs. Continuous monitoring allows for ongoing system improvements.
- Integrate with Other Business Systems: Connect the CMMS with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, procurement systems, and inventory management tools to streamline workflows and improve data accuracy.
- Perform Regular System Audits: Review CMMS usage periodically to identify gaps, improve efficiency, and adjust maintenance strategies. System audits help maintain long-term effectiveness.
Following these best practices ensures that a CMMS delivers measurable improvements in maintenance efficiency, cost savings, and asset performance. Proper planning and ongoing optimization help businesses maximize their return on investment while maintaining a well-organized and effective maintenance strategy.
Manufacturers worldwide are adopting cloud-based solutions to improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. At 42Q, we combine decades of manufacturing expertise with innovative technology to deliver smart connected manufacturing. Our flexible, cloud-native MES platform enhances visibility, streamlines operations, and accelerates digital factory transformation. Explore how our solutions can optimize your factory’s performance and drive measurable results.
Key Takeaways
- A CMMS automates preventive maintenance scheduling, reducing downtime and preventing unexpected equipment failures.
- Real-time asset tracking improves efficiency, helping maintenance teams diagnose and resolve issues faster.
- Automated work order management streamlines task assignments, improves communication, and enhances team productivity.
- Tracking maintenance costs and inventory prevents budget overruns and ensures essential supplies are always available.
- Data-driven reporting helps businesses analyze trends, optimize maintenance strategies, and improve long-term asset management.
FAQs
A CMMS improves maintenance efficiency by automating scheduling, tracking asset performance, and managing work orders. It reduces downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and helps control costs by optimizing resource allocation. Businesses also benefit from streamlined reporting, real-time data access, and better compliance with maintenance regulations.
Automated preventive maintenance schedules prevent costly emergency repairs and unexpected breakdowns. A CMMS tracks maintenance expenses, analyzes repair versus replacement costs, and ensures that parts and supplies are efficiently managed. This structured approach lowers unnecessary spending while extending the life of critical equipment.
Many CMMS solutions integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, procurement software, and inventory management tools. Integration ensures seamless data flow, allowing businesses to synchronize maintenance operations with broader financial and operational strategies. This connectivity enhances efficiency and eliminates manual data entry errors.
Manufacturing, healthcare, facility management, and transportation industries benefit significantly from CMMS implementation. Any organization that relies on machinery, equipment, or infrastructure maintenance can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize maintenance schedules with a CMMS.
A CMMS maintains detailed records of maintenance history, inspections, and repairs, helping businesses meet regulatory requirements. Digitized record-keeping ensures that compliance documentation is always up to date, simplifying audits and reducing the risk of penalties due to incomplete maintenance records.
The Role of MES in the Pharmaceutical Industry

The Role of MES in the Pharmaceutical Industry
"Pharmaceutical MES assists manufacturers in maintaining strict process controls, enforcing regulatory requirements, and ensuring product quality through electronic batch records (EBRs) and automated compliance tracking."
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) have become a critical tool for pharmaceutical manufacturers aiming to improve efficiency, maintain regulatory compliance, and ensure product quality.
The pharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulations, requiring manufacturers to implement precise process controls and detailed traceability systems. Traditional manual workflows often introduce errors, inefficiencies, and compliance risks that can lead to costly recalls or production delays. MES addresses these challenges by digitizing and automating core manufacturing processes, creating a data-driven approach that enhances production consistency and visibility.
With the rise of complex drug formulations, personalized medicine, and globalized supply chains, pharmaceutical companies must adopt technologies that provide real-time process monitoring, batch record management, and seamless integration with other enterprise systems. MES streamlines these functions by capturing and analyzing production data, ensuring that each step meets predefined quality standards. Implementing MES allows manufacturers to improve operational efficiency while minimizing risks associated with regulatory audits and product recalls. As the industry continues shifting toward digital transformation, MES is a foundation for scalable, automated, and highly controlled pharmaceutical manufacturing.
What is MES in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a critical role in modern pharmaceutical production by providing real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of manufacturing processes. These software-driven solutions bridge the gap between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and plant-floor operations, seamless data flow, and process automation.
Pharmaceutical MES assists manufacturers in maintaining strict process controls, enforcing regulatory requirements, and ensuring product quality through electronic batch records (EBRs) and automated compliance tracking. By integrating MES into pharmaceutical production, companies can improve traceability, reduce errors, and optimize workflows while meeting stringent regulatory standards.
MES solutions also enhance production visibility, allowing manufacturers to track materials, equipment, and personnel activities in real-time. This level of control is essential for maintaining consistency across production batches, minimizing deviations, and streamlining reporting processes to align with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Importance of MES in Pharma
Pharmaceutical manufacturing requires precise control, strict documentation, and compliance with global regulatory standards. MES supports these requirements by digitizing and automating production processes, reducing manual interventions, and minimizing human error.
Electronic batch records (EBRs) replace paper-based documentation, streamlining record-keeping and audit readiness. With MES, manufacturers can monitor production in real-time, ensuring that all steps meet predefined quality and compliance standards. The system automatically flags deviations, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to costly recalls or regulatory violations.
MES makes Process optimization easier, as the system captures and analyzes production data to identify inefficiencies. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to adjust workflows, reduce waste, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Automated workflows also shorten production cycles, accelerating time-to-market for new pharmaceutical products while maintaining strict quality control.
Benefits of Implementing MES in Pharmaceutical Industries
Pharmaceutical manufacturing requires strict control over production processes to ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Manual documentation and outdated systems introduce risks, including data inconsistencies, human errors, and compliance challenges. MES automates these processes, reducing the likelihood of mistakes and ensuring accurate tracking of materials, equipment, and personnel. By integrating MES into production workflows, pharmaceutical manufacturers gain real-time visibility into operations faster and improve overall efficiency. MES integrates seamlessly with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and laboratory information management systems (LIMS), creating a connected digital ecosystem that enhances manufacturing intelligence.
- Improved Compliance: Automates data collection and ensures accurate documentation to meet regulatory requirements, reducing audit risks and compliance-related delays. Digital batch records replace manual paperwork, ensuring every production step is recorded in real-time and easily accessible for audits. Automated workflows enforce adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs), minimizing the risk of non-compliance and regulatory scrutiny.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Enforces standardized procedures, reducing human error and ensuring consistent product integrity across all production batches. MES provides built-in quality control mechanisms, automatically flagging deviations from set parameters before defects occur.
- Real-Time Process Monitoring: Provides immediate insights into production performance, allowing operators to detect and address deviations before they impact product quality. MES continuously collects data from sensors, equipment, and production lines, offering a complete view of manufacturing operations. Alerts and notifications highlight temperature fluctuations, machine malfunctions, or unexpected process variations, ensuring quick corrective actions.
- Increased Efficiency: Reduces manual paperwork and streamlines workflows, leading to faster production cycles and optimized resource allocation. MES digitizes production records, reducing administrative burdens and freeing up time for value-added activities. Automated task sequencing ensures that production steps occur in the correct order, minimizing downtime and improving throughput.
- Reduced Waste and Rework: Identifies inefficiencies in production processes, minimizing material losses and improving overall yield rates. MES tracks raw material usage, reducing excess consumption and improving inventory management. Advanced analytics provide insights into recurring defects or inefficiencies, allowing manufacturers to optimize processes and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Seamless System Integration: Connects with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and laboratory information management systems (LIMS) to create a unified digital manufacturing framework. MES synchronizes production data across various departments, ensuring accurate material tracking, batch genealogy, and automated reporting. Integrating existing IT systems allows pharmaceutical manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce redundancy, and improve coordination between quality control, supply chain, and production teams.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers face mounting pressures to produce high-quality products while meeting regulatory requirements and maintaining cost efficiency. MES provides the tools to achieve these goals by offering real-time production insights, automating compliance tracking, and optimizing manufacturing workflows. Integrating MES with existing systems ensures a streamlined, data-driven approach to pharmaceutical production. Companies implementing MES gain an advantage through improved operational transparency, higher product reliability, and reduced risk of compliance-related setbacks. As manufacturing processes become more complex, MES remains a critical solution for improving efficiency, ensuring regulatory adherence, and maintaining high-quality production standards.
Core Components of Pharmaceutical MES
MES provides a structured approach to managing pharmaceutical production, integrating critical functionalities that enhance efficiency, compliance, and traceability. Each component is vital in optimizing operations and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
Electronic Batch Records (EBRs)
Electronic batch records replace paper-based documentation, improving accuracy, traceability, and compliance. The system automatically captures and stores production data, ensuring each batch follows predefined protocols. With automated record-keeping, manufacturers eliminate manual data entry errors and reduce the risk of missing critical compliance details. EBRs also simplify audits by providing digital access to historical production data, reducing the time and effort required for regulatory reviews.
Production Scheduling and Workflow Management
Efficient production scheduling ensures that manufacturing resources, including equipment, raw materials, and personnel, are optimized to prevent delays. MES provides intelligent scheduling tools that align production timelines with material availability, reducing downtime and improving workflow efficiency. Automated workflows enforce adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs), ensuring that each production step is executed according to regulatory requirements. These capabilities help manufacturers maintain a consistent production flow, minimize bottlenecks, and improve on-time delivery rates.
Quality and Compliance Monitoring
Maintaining product quality is essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing. MES integrates quality control functions that continuously monitor process parameters, ensuring that production remains within acceptable tolerances. The system automatically flags deviations, triggers corrective actions, and documents changes in compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). By enforcing quality assurance measures throughout production, MES helps manufacturers maintain batch consistency while meeting stringent industry regulations.
Material and Inventory Tracking
MES provides real-time visibility into raw materials, in-process components, and finished goods inventory. This level of tracking prevents material shortages, reduces waste, and ensures accurate stock management. Traceability features allow manufacturers to track the genealogy of each batch, linking raw material usage to final product shipments. This transparency is critical for compliance with traceability requirements, allowing manufacturers to address any issues related to material quality or sourcing quickly.
Equipment and Asset Management
Manufacturing equipment must function efficiently to maintain production schedules and product quality. MES integrates with equipment monitoring systems to track machine performance, schedule preventive maintenance, and reduce unplanned downtime. Predictive maintenance capabilities analyze equipment data to detect early signs of wear, allowing manufacturers to address issues before they cause production disruptions. Effective asset management ensures all equipment operates at peak efficiency, extending machine lifespan and reducing operational costs.
Data Analytics and Reporting
MES collects production data from multiple sources, transforming raw information into actionable insights. The system generates reports on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as yield rates, cycle times, and compliance metrics. Manufacturers use these insights to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and enhance. Advanced analytics capabilities also support continuous improvement initiatives, allowing companies to refine production strategies and maintain operational excellence.
Each MES component contributes to a more efficient, compliant, and data-driven pharmaceutical manufacturing process. By integrating these functionalities, manufacturers can improve process control, enhance product quality, and maintain regulatory compliance while optimizing operations.
Challenges Faced in Implementing MES in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical manufacturers recognize the benefits of MES, but integrating these systems comes with significant challenges. Technical limitations, regulatory requirements, and workforce adaptation must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition from manual or legacy systems to a digital manufacturing. Careful planning, investment in infrastructure, and proper training are necessary to overcome these obstacles.
- High Initial Costs: MES implementation requires a substantial financial commitment, covering software, hardware, IT infrastructure, and system customization. Many pharmaceutical manufacturers operate on tight budgets, and the cost of upgrading legacy systems can strain financial resources. Small and mid-sized manufacturers may struggle to allocate funds for MES while maintaining existing production lines.
- Complex System Integration: MES must seamlessly connect with enterprise resource planning (ERP), laboratory information management systems (LIMS), and various production control systems. Integrating MES with existing infrastructure presents a challenge, especially when dealing with legacy systems not initially designed for modern digital connectivity. Data silos, interoperability issues, and software incompatibilities often require extensive customization, leading to delays in implementation.
- Regulatory Compliance Adaptation: Pharmaceutical manufacturers must comply with strict regulations such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11, EU Annex 11, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). MES plays a key role in supporting compliance by automating documentation, enforcing batch traceability, and maintaining secure audit trails. However, configuring MES to align with specific regional and international regulatory requirements presents a challenge. Customization may be needed to ensure electronic signatures, automated reporting, and process validation meet legal standards.
- Employee Training and Adoption: Transitioning from manual or paper-based processes to an MES-driven production requires a shift in workforce skills and daily operations. Employees accustomed to traditional manufacturing methods may resist adopting digital workflows, especially if training programs are insufficient or lack hands-on engagement. The complexity of MES interfaces and functionalities can also present a learning curve for operators, technicians, and quality control personnel. Employees may struggle to use MES effectively without proper training, leading to operational inefficiencies and user errors.
- Customization and Scalability Issues: Pharmaceutical manufacturing processes vary significantly based on drug formulations, production volume, and regulatory requirements. A standard MES solution may not fully align with a manufacturer's specific needs, requiring customization to accommodate unique workflows and compliance protocols. Extensive customization can extend implementation timelines and increase costs, making it difficult to realize the benefits of MES in a reasonable timeframe.
- Data Security and Validation Requirements: MES manages highly sensitive production data, including batch records, equipment performance metrics, and compliance documentation. Protecting this data from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and potential corruption is essential for maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance. MES must include robust encryption, user authentication controls, and secure access protocols to prevent security breaches. System validation is also necessary to confirm that MES meets industry regulations and maintains accurate record-keeping standards. Regular audits, software updates, and IT security measures help safeguard MES against potential vulnerabilities.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers must approach MES implementation with a strategic plan that addresses these challenges. Assessing financial feasibility, aligning MES with existing infrastructure, ensuring regulatory compliance, and providing comprehensive workforce training are essential for a successful deployment. A well-implemented MES improves efficiency and product quality and strengthens compliance and production reliability in the long run.
Successful MES Implementations in Pharma
Pharmaceutical manufacturers implementing MES gain a significant advantage in optimizing operations, ensuring compliance, and improving overall efficiency. MES addresses long-standing challenges such as manual errors, process inefficiencies, and production inconsistencies, allowing companies to achieve greater accuracy and consistency in drug manufacturing. Regulatory agencies impose strict documentation and traceability requirements, and MES plays a crucial role in maintaining accurate records, streamlining compliance audits, and reducing the risk of regulatory penalties.
- Large-Scale Vaccine Production: A global pharmaceutical company implemented MES to manage high-volume vaccine production. The system automated batch records, reduced manual data entry errors, and improved compliance tracking, allowing for faster regulatory approvals. Given the urgency and scale of vaccine distribution, MES played a critical role in ensuring that production met stringent quality standards while expediting batch releases.
- Gene and Cell Therapy Manufacturing: A biotech firm specializing in personalized medicine adopted MES to ensure precise process control. The system real-time monitoring of patient-specific treatments, reducing deviations and enhancing traceability. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical manufacturing, gene and cell therapy processes require extreme precision, as each batch may be tailored to an individual patient.
- Sterile Injectable Production: A manufacturer of sterile injectables integrated MES to improve batch release times. Electronic batch records reduced paperwork processing, cutting the release cycle from several days to a few hours. In sterile manufacturing, contamination risks must be minimized, and MES provides real-time al monitoring and automated reporting to ensure compliance with GMP regulations.
- Multi-Site API Manufacturing: An active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) supplier deployed MES across multiple facilities to standardize production workflows. The system provided centralized data visibility, ensuring uniform compliance with global regulatory standards. API manufacturing involves complex chemical processes that require strict control over raw material quality, reaction conditions, and final product specifications.
- Contract Manufacturing Organization (CMO) Optimization: A contract manufacturer integrated MES to handle multiple client requirements while maintaining strict quality standards. Automated workflows and digital documentation streamlined production across various drug formulations. CMOs must manage production from numerous pharmaceutical clients, each with different regulatory expectations.
- Compliance Enhancement for an Oncology Drug Manufacturer: A pharmaceutical company producing oncology treatments adopted MES to improve adherence to GMP regulations. The system automated deviation tracking, reducing the risk of compliance-related production delays. Oncology drug manufacturing requires stringent controls due to the toxicity and potency of active ingredients.
Successful MES adoption depends on aligning system capabilities with production goals, regulatory requirements, and operational workflows. Pharmaceutical companies integrating MES effectively can streamline manufacturing processes while maintaining complete traceability across production batches. From vaccine production to personalized medicine, MES solutions help companies maintain quality control, standardize processes, and ensure seamless compliance with regulatory standards. As the industry moves toward increased automation and digitalization, MES will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Future Trends for MES in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Advancements in digital manufacturing continue to shape the future of MES in pharmaceutical production. As regulations tighten and production complexity increases, manufacturers seek solutions that enhance efficiency, improve compliance, and support data-driven. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming integral to MES by optimizing predictive maintenance, process monitoring, and quality control. AI-driven analytics provide deeper insights into production trends, helping manufacturers reduce waste and enhance operational efficiency. Cloud-based MES solutions are also gaining adoption, offering scalability and real-time access to production data across multiple facilities.
Pharmaceutical companies are integrating MES with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to improve real-time equipment monitoring and automation. Smart sensors and connected devices track production parameters with greater precision, reducing manual interventions and enhancing process control. Blockchain technology is also being explored to strengthen data integrity, ensuring tamper-proof batch records and supply chain transparency. Regulatory agencies continue to emphasize data integrity, driving the adoption of electronic batch records and digital signatures within MES. These systems will be crucial in maintaining compliance with Good Automated Manufacturing Practice (GAMP) guidelines, ensuring that all production data is securely stored and easily auditable.
Future MES advancements will focus on increasing automation, integrating emerging technologies, and improving interoperability with other manufacturing systems. These innovations will help pharmaceutical companies enhance product quality, streamline operations, and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers must adopt advanced solutions to meet production while maintaining precision and compliance. At 42Q, we deliver smart connected manufacturing with a cloud-based MES platform that enhances visibility, automates workflows, and accelerates production efficiency. Our flexible, scalable solutions give manufacturers real-time insights to optimize processes and meet regulatory requirements. Discover how 42Q can support your digital manufacturing strategy and drive efficiency in pharmaceutical production.
Key Takeaways
- MES enhances compliance and traceability by digitizing batch records, enforcing procedural adherence, and ensuring regulatory audit readiness.
- Real-time process monitoring reduces errors and improves efficiency, allowing manufacturers to detect and correct deviations before they impact product quality.
- MES minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization by automating workflows, reducing manual interventions, and streamlining production scheduling.
- Integration with existing manufacturing systems seamless data exchange between MES, ERP, LIMS, and quality management systems for improved operational visibility.
- Implementing MES supports scalability and automation, helping pharmaceutical companies adapt to regulatory requirements and increasing production complexity.
FAQs
MES helps pharmaceutical manufacturers maintain regulatory compliance by automating batch record management, enforcing procedural adherence, and generating audit-ready documentation. The system ensures data integrity, reduces human errors, and simplifies compliance with industry regulations such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and EU Annex 11.
MES minimizes material waste and rework by providing real-time data on production performance and batch deviations. The system detects inefficiencies, optimizes resource allocation, and prevents overproduction, ensuring that materials are utilized efficiently while maintaining product quality.
MES integrates seamlessly with enterprise resource planning (ERP), laboratory information management systems (LIMS), and quality management systems (QMS). This connectivity allows manufacturers to streamline operations, maintain accurate inventory tracking, and enhance process automation across the entire production cycle.
When implementing MES, pharmaceutical manufacturers must consider system compatibility, regulatory compliance, workforce training, and long-term scalability. Ensuring that MES aligns with existing workflows and production goals is crucial for maximizing its benefits and achieving a smooth transition from manual processes.
MES continuously collects and analyzes production data from equipment, sensors, and batch records for real-time monitoring. Operators receive instant alerts on process deviations, equipment malfunctions, or quality concerns, proactively minimizing production disruptions.
